4-Brompyridin
4-Brompyridin ist eine organische Verbindung, die zu den Heterocyclen (genauer: Heteroaromaten) zählt. Sie besteht aus einem Pyridinring, der in 4-Position mit Brom substituiert ist. Die Verbindung ist isomer zu 2-Brompyridin und 3-Brompyridin.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
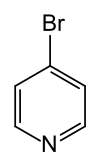 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | 4-Brompyridin | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C5H4BrN | |||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
farblose Flüssigkeit, weißer, nicht-hygroskopischer Feststoff als Hydrochlorid[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 158,00 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig | |||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Dipolmoment | ||||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,5694 (20 °C)[3] | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | ||||||||||||||||
Darstellung
4-Brompyridin kann in sehr guter Ausbeute durch Diazotierung von 4-Aminopyridin und anschließender Substitution mit Brom und Bromwasserstoffsäure erhalten werden.[1]
Verwendung
2,4′-Bipyridin kann durch eine Negishi-Kupplung aus 2-Brompyridin und 4-Brompyridin hergestellt werden. Hierzu wird 2-Brompyridin zunächst mit n-Butyllithium lithiiert und unter Zugabe von Zinkchlorid zum Zinkorganyl transmetalliert. Als Katalysator zur Kupplung dient ein Palladiumkomplex mit Triphenylphosphanliganden.[5]
Einzelnachweise
- A. Murray III, W. H. Langham: A Synthesis of Isonicotinic Acid by Halogen–Metal Exchange and Its Application to the Preparation of Isonicotinic-C14 Acid Hydrazide, in: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1952, 74, S. 6289–6290; doi:10.1021/ja01144a515.
- C. W. N. Cumper, A. I. Vogel: Physical properties and chemical constitution. Part XXX. The dipole moments of some halogeno- and cyano-pyridines, in: J. Chem. Soc., 1960, S. 4723–4728; doi:10.1039/JR9600004723.
- David R. Lide (Hrsg.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 90. Auflage. (Internet-Version: 2010), CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, S. 3-70.
- Datenblatt 4-Brompyridiniumchlorid (PDF) bei Merck, abgerufen am 6. September 2012.
- D. R. Sidler, N. Barta, W. Li, E. Hu, L. Matty, N. Ikemoto, J. S. Campbell, M. Chartrain, K. Gbewonyo, R. Boyd, E. G. Corley, R. G. Ball, R. D. Larsen, P. J. Reider, Paul J: Efficient synthesis of the optically active dihydropyrimidinone of a potent α1A-selective adrenoceptor antagonist. In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 80 (6), 2002, S. 646–652, doi:10.1139/v02-079.
