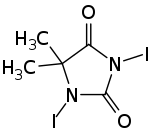
1,3-Diiod-5,5-dimethylhydantoin
1,3-Diiod-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (kurz DIH) ist eine heterocyclische organische Verbindung, die in der organischen Synthese als Iodierungsreagenz sowie als Oxidationsmittel eingesetzt wird.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | 1,3-Diiod-5,5-dimethylhydantoin | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C5H6I2N2O2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung | |||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 379,92 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
löslich in Aceton, gering löslich in Dichlormethan[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||||||||
Gewinnung und Darstellung
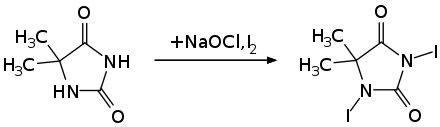
Die Herstellung von 1,3-Diiod-5,5-dimethylhydantoin erfolgte erstmals 1965 durch die Umsetzung von Iodmonochlorid mit 5,5-Dimethylhydantoin in Gegenwart von Natronlauge.[4] Das Edukt 5,5-Dimethylhydantoin kann sehr einfach aus Kaliumcyanat, Ammoniumcarbonat und Aceton kommerziell synthetisiert werden.[1] Eine neuere Synthese nutzt die Kombination aus Iod und Kaliumiodid als Iodquelle und Natriumhypochlorit als Oxidationsmittel.[5][2]
Eigenschaften
1,3-Diiod-5,5-dimethylhydantoin bildet ein schwach gelbes bis hellbraunes Pulver, das bei 192–196 °C unter Zersetzung schmilzt. Es ist bei −20 °C lagerstabil. Die Verbindung löst sich gut in Aceton, wobei bei Temperaturen oberhalb von 50 °C eine Reaktion unter Bildung von Iodaceton stattfindet. Zudem ist der Stoff licht- und feuchtigkeitsempfindlich.[1]
Verwendung
1,3-Diiod-5,5-dimethylhydrandoin wird in der organischen Synthese als Iodierungsreagenz und Oxidationsmittel eingesetzt. In einer electrophilen Iodierung können elektronenreiche Aromaten und Heteroaromaten umgesetzt werden.[6] Hierbei werden beide Iodatome genutzt. Im Vergleich zur Verwendung von elementarem Iod entsteht kein Iodwasserstoff. Anilin wird zum 4-Iodanilin, Phenol zum 2,4,6-Triiodphenol umgesetzt.[1] Primäre Alkohole können in Gegenwart von Ammoniak zu den entsprechenden Nitrilen oxidiert werden. Aus substituierten Benzylalkoholen resultieren die entsprechenden Benzonitrile. In ähnlicher Weise können auch primäre, sekundäre und ternäre Amine, sowie Halogenide und Aldehyde zu Nitrilen umgesetzt werden.[1][7][8][9]
Substituierte Benzaldehyde können mit sekundären Aminen in Gegenwart von 1,3-Diiod-5,5-dimethylhydrandoin in einer oxydativen Aminierung zu den entsprechenden Benzamiden umgesetzt werden.[10][2]

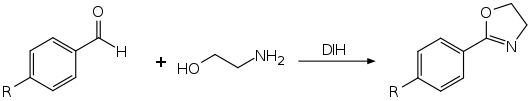
In ähnlicher Weise sind durch die Reaktion von Benzaldehyden mit Ethanolamin in Gegenwart von 1,3-Diiod-5,5-dimethylhydrandoin in 2-Stellung substituierte Oxazoline zugänglich.[11][1][2]
Es können analog weitere substituierte Heterocyclen synthetisiert werden.[1] Die Umsetzung mit 1,3-Propandiamin ergibt in 2-Stellung substituierte 1,4,6,6-Tetrahydropyrimidine, die zu den entsprechenden Pyrimidinen weiteroxidiert werden können.[12] 3-Phenyl-1-propanol kann zum Chroman zyklisiert werden.[13]
Einzelnachweise
- 1,3-Diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. In: e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley and Sons, 1999–2013, abgerufen am 19. Dezember 2017.
- C. Ricco: 1,3-Diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. In: Synlett. 24, 2013, S. 2173–2174, doi:10.1055/s-0033-1339477.
- Datenblatt 1,3-Diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 19. Dezember 2017 (PDF).
- O. O. Orazi, R. A. Corral, H. E. Bertorello: N-Iodohydantoins. II. Iodinations with 1,3-Diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. In: J. Org. Chem. 30, 1965, S. 1101–1104, doi:10.1021/jo01015a036.
- K Mima. Japanese Patent 2013/23475, 2013.
- V. K. Chaikovskii, V. D. Filimonov, A. A. Funk, V. I. Skorokhodov, V. D. Ogorodnikov: 1,3-Diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin—An efficient reagent for iodination of aromatic compound. In: Russian J. Org. Chem. 43, 2007, S. 1291–1296, doi:10.1134/S1070428007090060
- S. Iida, H. Togo: Oxidative Conversion of Primary Alcohols, and Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Amines into the Corresponding Nitriles with 1,3-Diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin in Aqueous NH3. In: Synlett. 2007, S. 407–410, doi:10.1055/s-2007-967954.
- S. Iida, H. Togo: Direct oxidative conversion of alcohols and amines to nitriles with molecular iodine and DIH in aq NH3. In: Tetrahedron. 63, 2007, S. 8274–8281, doi:10.1016/j.tet.2007.05.106.
- S. Iida, R. Ohmura, H. Togo: Direct oxidative conversion of alkyl halides into nitriles with molecular iodine and 1,3-diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin in aq ammonia. In: Tetrahedron. 65, 2009, S. 6257–6262, doi:10.1016/j.tet.2009.05.001.
- H. Baba, K. Moriyama, H. Togo: Preparation of N,N-Dimethyl Aromatic Amides from Aromatic Aldehydes with Dimethylamine and Iodine Reagents. In: Synlett. 23, 2012, S. 1175–1180, doi:10.1055/s-0031-1290659.
- S. Takahashi, H. Togo: An Efficient Oxidative Conversion of Aldehydes into 2-Substituted 2-Oxazolines Using 1,3-Diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. In: Synthesis. 2009, S. 2329–2332, doi:10.1055/s-0029-1216843.
- S. Takahashi, H. Togo: Direct Oxidative Conversion of Aldehydes into 2-Substituted 1,4,5,6-Tetrahydropyrimidines Using Molecular Iodine or 1,3-Diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. In: Heterocycles. 82, 2010, S. 593–601, doi:10.3987/COM-10-S(E)29.
- S. Furuyama, H. Togo: An Efficient Preparation of Chroman Derivatives from 3-Aryl-1-propanols and Related Compounds with 1,3-Diiodo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin under Irradiation Conditions. In: Synlett. 2010, S. 2325–2329, doi:10.1055/s-0030-1258017.