Phenylethylamine
Als Phenylethylamine (auch Phenylalkylamine oder β-Phenylalkylamine) bezeichnet man eine Gruppe chemischer Verbindungen, die sich vom Phenylethylamin ableiten. Zahlreiche Phenylethylamine besitzen eine weite Verbreitung in der Natur (z. B. Tyramin und Dopamin), während andere künstlichen Ursprungs sind (z. B. Amphetamin).
Natürlich vorkommende Phenylethylamine besitzen beispielsweise als L-Aminosäuren (L-Tyrosin und L-Phenylalanin) eine grundlegende Bedeutung für das Leben. Im menschlichen und tierischen Organismus spielen Phenylethylamine darüber hinaus eine wichtige Rolle als Neurotransmitter (z. B. Dopamin) und Hormone (z. B. Adrenalin). Viele im Pflanzenreich vorkommende Alkaloide sind ebenfalls den Phenylethylaminen zuzuordnen (z. B. Ephedrin, Mescalin).
Synthetisch hergestellte Phenylethylamine, wie z. B. der Calciumantagonist Verapamil oder Etilefrin, finden als Arzneimittel Anwendung. Zahlreiche Verbindungen dieser Stoffgruppe besitzen psychotrope Eigenschaften.
Die wesentlichen Strukturmerkmale von Phenylethylaminen und Tryptaminen finden sich in den Lysergsäureamiden vereint.[1]
Phenylethylamine
- Phenethylamin (PEA)
- β-Methylphenethylamin (BMPEA, 1-Amino-2-phenylpropan)
- 4-Hydroxyphenylethylamin (Tyramin)
- 1-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-(ethylamino)ethanol (Etilefrin)
- 1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)ethanol (Synephrin)
- 4-(2-Amino-1-hydroxy-ethyl)phenol (Norsynephrin)
- Methylphenidat (MPH; Handelsname u. a. Ritalin)
Katecholamine
- Adrenalin
- Noradrenalin
- Dopamin (3,4-Dihydroxy-β-phenylethylamin)
- Isoprenalin
- Orciprenalin
- Dobutamin
- Reproterol
- Terbutalin
- Dopexamin
- Metanephrine
Methoxyphenylethylamine
2,5-Dimethoxyphenylethylamine
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-bromphenethylamin (2C-B)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-chlorphenethylamin (2C-C)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylphenylethylamin (2C-D)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylphenylethylamin (2C-E)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-propylphenethylamin (2C-P)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodphenethylamin (2C-I)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-fluorphenethylamin (2C-F)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitrophenethylamin (2C-N)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylthiophenylethylamin (2C-T-2)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(iso)-propylthiophenylethylamin (2C-T-4)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(n)-propylthiophenylethylamin (2C-T-7)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-cyclopropylmethylthiophenylethylamin (2C-T-8)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-butylthiophenylethylamin (2C-T-9)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(2-fluorethylthio)phenylethylamin (2C-T-21)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluormethylphenethylamin (2C-TFM)
3,4-Dimethoxyphenethylamin
Trimethoxyphenylethylamine
- 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenylethylamin (Meskalin, M)
- 2,3,4-Trimethoxyphenylethylamin (IM)
- 2,4,5-Trimethoxyphenylethylamin (TMPEA)
Amphetamine
(Trivialbezeichnung für 1-Phenyl-2-aminopropane)
- Amphetamin
- N-Methylamphetamin (Methamphetamin)
- Ephedrin, Pseudoephedrin
- Norephedrin, Norpseudoephedrin
- 4-Hydroxyephedrin (Oxilofrin)
- N-Methylephedrin
- N-Ethylamphetamin
- 4-Methoxyamphetamin (PMA)
- 4-Methoxy-N-methylamphetamin (PMMA, Methyl-MA)
- Tiflorex
- Lisdexamfetamin (Handelsname „Elvanse“)
Cathinone
- Cathinon (β-Keto-amphetamin)
- N-Methylcathinon (Methcathinon, Ephedron)
- 4-Methylmethcathinon (4-MMC, Mephedron)
- 4-Methylethcathinon (4-MEC)
- Pentedron
- 3,4-Methylendioxycathinon (bk-MDA, MDC)
- 3,4-Methylendioxy-N-ethylcathinon (bk-MDEA, MDEC, Ethylon)
- 3,4-Methylendioxy-N-methylcathinon (bk-MDMA, MDMC, Methylon)
- 3,4-Methylendioxypyrovaleron (MDPV)
- Pyrovaleron
- 3-Chlor-N-tert-butylcathinon (Bupropion)
- 2-Diethylamino-1-phenylpropan-1-on (Diethylpropion, Amfepramon)
Dimethoxyamphetamine
- 3,4-Dimethoxyamphetamin (3,4-DMA)
- 2,5-Dimethoxyamphetamin (2,5-DMA)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-bromamphetamin (DOB)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodamphetamin (DOI)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamin (DOM, STP)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitroamphetamin (DON)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-chloramphetamin (DOC)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-fluoramphetamin (DOF)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylamphetamin (DOET)
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-propylamphetamin (DOPR)
Methylendioxyamphetamine
- 3,4-Methylendioxyamphetamin (MDA)
- 3,4-Methylendioxy-N-methylamphetamin (MDMA)
- 3,4-Methylendioxy-N-ethylamphetamin (MDEA, MDE)
- 2-Methoxy-3,4-methylendioxyamphetamin (MMDA-3a)
- 3-Methoxy-4,5-methylendioxyamphetamin (MMDA)
Trimethoxy- und Trialkoxyamphetamine
- 3,4,5-Trimethoxyamphetamin (TMA)
- 2,4,5-Trimethoxyamphetamin (TMA-2)
- 2,3,4-Trimethoxyamphetamin (TMA-3)
- 2,3,5-Trimethoxyamphetamin (TMA-4)
- 2,3,6-Trimethoxyamphetamin (TMA-5)
- 2,4,6-Trimethoxyamphetamin (TMA-6)
- 3,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethoxyamphetamin (3C-E)
1-Phenyl-2-aminobutane
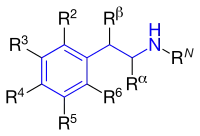
Übersicht
 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | RN | Rα | Rβ | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | chemischer Name |
| Tyramin | H | H | H | H | H | –OH | H | H | 4-Hydroxy-phenethylamin |
| Dopamin | H | H | H | H | –OH | –OH | H | H | 3,4-Dihydroxy-phenethylamin |
| Adrenalin | –CH3 | H | –OH | H | –OH | –OH | H | H | β,3,4-Trihydroxy-N-methyl-phenethylamin |
| Noradrenalin | H | H | –OH | H | –OH | –OH | H | H | β,3,4-Trihydroxy-phenethylamin |
| Synephrin | –CH3 | H | –OH | H | H | –OH | H | H | β,4-Dihydroxy-N-methyl-phenethylamin |
| Etilefrin | –CH2–CH3 | H | –OH | H | –OH | H | H | H | β,3-Dihydroxy-N-ethyl-phenethylamin |
| Norsynephrin | H | H | –OH | H | H | –OH | H | H | β,4-Dihydroxy-phenethylamin |
| Phenylephrin | –CH3 | H | –OH | H | –OH | H | H | H | β,3-Dihydroxy-N-methyl-phenethylamin |
| Salbutamol | –C(CH3)3 | H | –OH | H | –CH2OH | –OH | H | H | 2-(tert-Butylamino)-1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)ethanol |
| Methylphenidat | –CH2–CH2–CH2–CH2– | –C(OCH3)=O | H | H | H | H | H | N,α-Butylen-β-methoxycarbonyl-phenethylamin | |
| Ethylphenidat | –CH2–CH2–CH2–CH2– | –C(OCH2–CH3)=O | H | H | H | H | H | N,α-Butylen-β-ethoxycarbonyl-phenethylamin | |
| Amphetamin | H | –CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | α-Methyl-phenethylamin |
| 4-Fluoramphetamin | H | –CH3 | H | H | H | –F | H | H | 4-Fluor-α-methyl-phenethylamin |
| 4-Chloramphetamin | H | –CH3 | H | H | H | –Cl | H | H | 4-Chlor-α-methyl-phenethylamin |
| 4-Bromamphetamin | H | –CH3 | H | H | H | –Br | H | H | 4-Brom-α-methyl-phenethylamin |
| 4-Iodamphetamin | H | –CH3 | H | H | H | –I | H | H | 4-Iod-α-methyl-phenethylamin |
| 4-Methoxyamphetamin | H | –CH3 | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | H | 4-Methoxy-α-methyl-phenethylamin |
| 4-Methylthioamphetamin | H | –CH3 | H | H | H | –SCH3 | H | H | 4-Methylthio-α-methyl-phenethylamin |
| Methamphetamin | –CH3 | –CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | N-Methyl-amphetamin |
| 4-Fluormethamphetamin | –CH3 | –CH3 | H | H | H | –F | H | H | 4-Fluor-N-methyl-amphetamin |
| Ephedrin, Pseudoephedrin | –CH3 | –CH3 | –OH | H | H | H | H | H | N-Methyl-β-hydroxy-amphetamin |
| Oxilofrin | –CH3 | –CH3 | –OH | H | H | –OH | H | H | 4-Hydroxy-ephedrin |
| Cathin | H | –CH3 | –OH | H | H | H | H | H | β-Hydroxy-amphetamin |
| Cathinon | H | –CH3 | =O | H | H | H | H | H | β-Keto-amphetamin |
| Methcathinon | –CH3 | –CH3 | =O | H | H | H | H | H | N-Methyl-β-keto-amphetamin |
| Bupropion | –C(CH3)3 | –CH3 | =O | H | –Cl | H | H | H | 3-Chlor-N-tert-butyl-β-keto-amphetamin |
| Fenfluramin | –CH2CH3 | –CH3 | H | H | –CF3 | H | H | H | 3-Trifluormethyl-N-ethyl-amphetamin |
| Phentermin | H | –CH3,–CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | α,α-Dimethyl-phenethylamin |
| MDA | H | –CH3 | H | H | –O–CH2–O– | H | H | 3,4-Methylendioxy-amphetamin | |
| βk-MDA | H | –CH3 | =O | H | –O–CH2–O– | H | H | 3,4-Methylendioxy-β-keto-amphetamin | |
| MDMA | –CH3 | –CH3 | H | H | –O–CH2–O– | H | H | 3,4-Methylendioxy-N-methyl-amphetamin | |
| βk-MDMA | –CH3 | –CH3 | =O | H | –O–CH2–O– | H | H | 3,4-Methylendioxy-N-methyl-β-keto-amphetamin | |
| MDEA | –CH2CH3 | –CH3 | H | H | –O–CH2–O– | H | H | 3,4-Methylendioxy-N-ethyl-amphetamin | |
| βk-MDEA | –CH2CH3 | –CH3 | =O | H | –O–CH2–O– | H | H | 3,4-Methylendioxy-N-ethyl-β-keto-amphetamin | |
| 5-APB | H | –CH3 | H | H | –CH=CH–O– | H | H | 5-(2-Aminopropyl)benzofuran | |
| 6-APB | H | –CH3 | H | H | –O–CH=CH– | H | H | 6-(2-Aminopropyl)benzofuran | |
| Name | RN | Rα | Rβ | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | chemischer Name |
 | |||||||||
| Name | RN | Rα | Rβ | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | chemischer Name |
| Mescalin | H | H | H | H | –OCH3 | –OCH3 | –OCH3 | H | 3,4,5-Trimethoxy-phenethylamin |
| TMA | H | –CH3 | H | H | –OCH3 | –OCH3 | –OCH3 | H | 3,4,5-Trimethoxy-amphetamin |
| TMA-2 | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | H | –OCH3 | –OCH3 | H | 2,4,5-Trimethoxy-amphetamin |
| TMA-3 | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | –OCH3 | –OCH3 | H | H | 2,3,4-Trimethoxy-amphetamin |
| TMA-4 | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | –OCH3 | H | –OCH3 | H | 2,3,5-Trimethoxy-amphetamin |
| TMA-5 | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | –OCH3 | H | H | –OCH3 | 2,3,6-Trimethoxy-amphetamin |
| TMA-6 | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | H | –OCH3 | H | –OCH3 | 2,4,6-Trimethoxy-amphetamin |
| DOM | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | H | –CH3 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methyl-amphetamin |
| DOB | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | H | –Br | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-brom-amphetamin |
| DOI | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | H | –I | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iod-amphetamin |
| DON | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | H | –NO2 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitro-amphetamin |
| DOC | H | –CH3 | H | –OCH3 | H | –Cl | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-chlor-amphetamin |
| 2C-B | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –Br | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-brom-phenethylamin |
| βk-2C-B | H | H | =O | –OCH3 | H | –Br | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-brom-β-keto-phenethylamin |
| 2C-C | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –Cl | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-chlor-phenethylamin |
| 2C-I | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –I | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iod-phenethylamin |
| 2C-D | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –CH3 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methyl-phenethylamin |
| 2C-E | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –CH2CH3 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethyl-phenethylamin |
| 2C-P | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –CH2CH2CH3 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-propyl-phenethylamin |
| 2C-F | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –F | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-fluor-phenethylamin |
| 2C-N | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –NO2 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitro-phenethylamin |
| 2C-T-2 | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –SCH2CH3 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylthio-phenethylamin |
| 2C-T-4 | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –SCHCH3CH3 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iso-propylthio-phenethylamin |
| 2C-T-7 | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –SCH2CH2CH3 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-propylthio-phenethylamin |
| 2C-T-8 | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –SCH2CHCH2CH2 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-cyclopropylmethylthio-phenethylamin |
| 2C-T-9 | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –S(CH3)3C | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-tert-butylthio-phenethylamin |
| 2C-T-21 | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –SCH2CH3–F | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(2-fluorethylthio)-phenethylamin |
| 2C-TFM | H | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –CF3 | –OCH3 | H | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluormethyl-phenethylamin |
| 25I-NBOMe | –CH2–C6H4–OCH3 | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –I | –OCH3 | H | N-(2-Methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iod-phenethylamin |
| 25C-NBOMe | –CH2–C6H4–OCH3 | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –Cl | –OCH3 | H | N-(2-Methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlor-phenethylamin |
| 25B-NBOMe | –CH2–C6H4–OCH3 | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –Br | –OCH3 | H | N-(2-Methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-brom-phenethylamin |
| 25D-NBOMe | –CH2–C6H4–OCH3 | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –CH3 | –OCH3 | H | N-(2-Methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl-phenethylamin |
| 25E-NBOMe | –CH2–C6H4–OCH3 | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –CH2CH3 | –OCH3 | H | N-(2-Methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethyl-phenethylamin |
| 25N-NBOMe | –CH2–C6H4–OCH3 | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –NO2 | –OCH3 | H | N-(2-Methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro-phenethylamin |
| 25I-NBOH | –CH2–C6H4–OH | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –I | –OCH3 | H | N-(2-Hydroxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iod-phenethylamin |
| 25C-NBOH | –CH2–C6H4–OH | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –Cl | –OCH3 | H | N-(2-Hydroxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlor-phenethylamin |
| 25B-NBOH | –CH2–C6H4–OH | H | H | –OCH3 | H | –Br | –OCH3 | H | N-(2-Hydroxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-brom-phenethylamin |
| Name | RN | Rα | Rβ | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | chemischer Name |
 | |||||||||
Grafische Übersicht

Übersicht über eine kleine Auswahl an endogenen, natürlichen und synthetischen Phenylalkylaminen, inklusive einiger Ausgangs- und Abbaustoffe
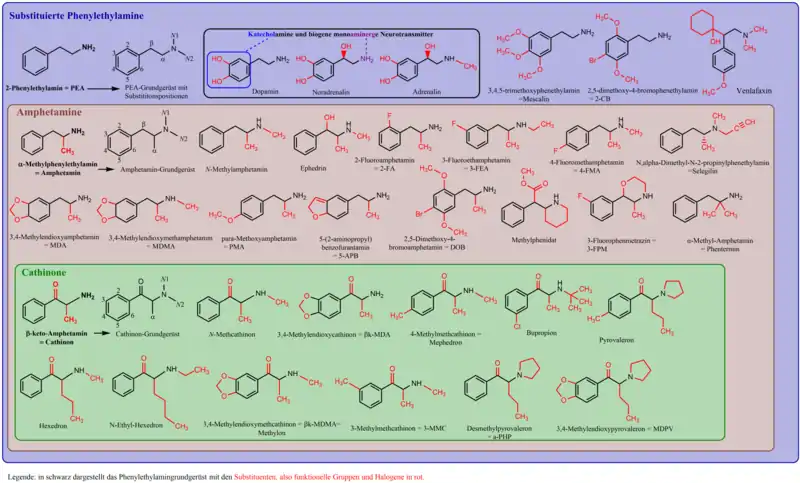
Übersicht über ausgewählte Phenylethylamine mit dem 2-Phenethylamin als Stammverbindung. Dargestellt sind die Strukturformeln in schwarz und ausgehend von der Stammverbindung in rot die Substituenten, also die Änderungen an der Struktur, meist funktionelle Gruppen oder Halogene. Ebenso die gebildeten Untergruppen mit ähnlicher Struktur und Eigenschaft werden gezeigt.
Siehe auch
Literatur
- D. Trachsel, D. Lehmann, Ch. Enzensperger: Phenethylamine Von der Struktur zur Funktion. Nachtschatten Science-Edition, Solothurn, Schweiz, 2013, ISBN 978-3-03788-700-4.
- Alexander Shulgin, Ann Shulgin: PIHKAL – A Chemical Love Story. Transform Press, Berkeley 1995, ISBN 0-9630096-0-5.
- Stephen J. Chapman: Novel Psychoactive Spectra: NMR of (mostly) Novel Psychoactive Substances – BLOTTER. In: isomerdesign.com. 25. Juni 2018, abgerufen am 26. Januar 2019 (englisch).
Weblinks
- PIHKAL online – via erowid (englisch)
Einzelnachweise
- Fabrizio Schifano, Laura Orsolini, Duccio Papanti, John Corkery: NPS: Medical Consequences Associated with Their Intake. In: Michael H. Baumann, Richard A. Glennon, Jenny L. Wiley: Neuropharmacology of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS). Springer, eBook 2016, ISBN 978-3-319-52444-3, S. 364.