Thymidylat-Synthase
Thymidylat-Synthase ist ein Enzym der Biosynthese von dTMP, (d für Desoxynukleotide; TMP für Thymidinmonophosphat) das Uracil in Form von Uridinmonophosphat methyliert. Die Anwesenheit ausreichender Mengen dTMP ist notwendig für die DNA-Reparatur und ihre Replikation. Das Enzym ist daher Target für Zytostatika wie 5-Fluoruracil, Tegafur, Capecitabin, Methotrexat, Pemetrexed und Raltitrexed, die es hemmen.[1] Resistenzen gegen diese Medikamente treten in Personen auf, die einen Überschuss des Enzyms produzieren. TYMS konkurriert mit dem Enzym MTHFR, das Homocystein zu Methionin umwandelt, um den Kofaktor Methylen-Tetrahydrofolat.[2]
| Thymidylat-Synthase | ||
|---|---|---|
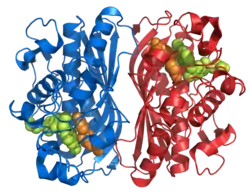 | ||
| Bändermodell des Thymidylat-Synthase-Dimer, komplexiert mit dem Inhibitor Raltitrexed (Kalotten) nach PDB 1HVY | ||
|
Vorhandene Strukturdaten: 1hvy, 1hw3, 1hw4, 1hzw, 1i00, 1ju6, 1juj, 1ypv, 2onb | ||
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 313 aa; 35,7 kDa | |
| Sekundär- bis Quartärstruktur | Homodimer | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Gen-Namen | TYMS ; TS; HsT422; MGC88736; TMS; TSase | |
| Externe IDs | ||
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 2.1.1.45, Transferase | |
| Reaktionsart | Reduktive Methylierung | |
| Substrat | dUMP + 5,10-Methylentetrahydrofolat | |
| Produkte | dTMP + Dihydrofolat | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Lebewesen | |
| Orthologe | ||
| Mensch | Maus | |
| Entrez | 7298 | 22171 |
| Ensembl | ENSG00000176890 | ENSMUSG00000025747 |
| UniProt | P04818 | Q544L2 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_001071 | NM_021288 |
| Refseq (Protein) | NP_001062 | NP_067263 |
| Genlocus | Chr 18: 0.65 – 0.66 Mb | Chr 5: 30.39 – 30.4 Mb |
| PubMed-Suche | 7298 | 22171 |
Synthese
Das für TYMS codierende Gen ist in allen Eukaryoten zu finden. Es erstreckt sich beim Menschen in 6 Exons über 15 Kilobasen auf Chromosom 18. Das Protein ist 313 Aminosäuren lang und 35,7 kDa schwer.[3]
Katalysierte Reaktion
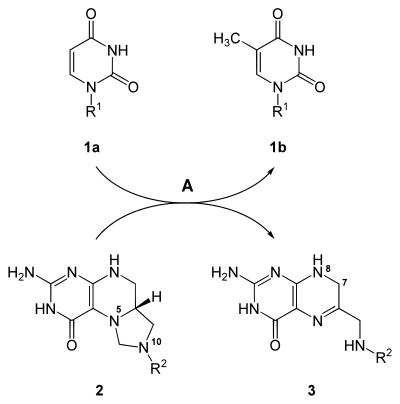 Die durch TYMS katalysierte Reaktion
Die durch TYMS katalysierte Reaktion
Die Synthese von dTMP (1b) aus dUMP (1a) wird durch die Thymidylat-Synthase (A) katalysiert. Die Methylgruppe stammt aus N5,N10-Methylentetrahydrofolat (2), das zu 7,8-Dihydrofolat (3) umgesetzt wird. Beim Rest R1 handelt es sich um 1-(2-Desoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-, R2 ist -benzoylglutaminsäure.
Medizinische Bedeutung
Thymidilat-Synthase wird gehemmt vom Zytostatikum 5-Fluorouracil, das vor allem bei kolorektalen Karzinomen und Magenkarzinomen eingesetzt wird.
Einzelnachweise
- Seymour S. Cohen, Joel G. Flaks, Hazel D. Barner, Marilyn R. Loeb, Janet Lichtenstein: The Mode of Action of 5-Fluorouracil and Its Derivatives. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Band 44, Nr. 10, 15. Oktober 1958, ISSN 0027-8424, S. 1004–1012, doi:10.1073/pnas.44.10.1004, PMID 16590300 (pnas.org [abgerufen am 2. Juni 2018]).
- Thymidylat-Synthase. In: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. (englisch).
- Ensembl-Eintrag