Salsolinol
Salsolinol ist ein Isochinolin-Alkaloid, das als Racemat mit bis zu 25 µg/g in Schokolade, Kakao und Bananen vorkommt[3], aber auch im Organismus endogen gebildet werden kann. Salsolinol hemmt verschiedene Enzyme, beispielsweise die Monoamin-Oxidase und die Tyrosinhydroxylase. Es ist in höheren Konzentrationen neurotoxisch, und der Verdacht wurde erhoben, dass ihm eine wichtige Rolle bei der Pathogenese der Parkinson-Krankheit zukommt.[4][5] Die Ursachen der Neurotoxizität sind ansatzweise bekannt. So spielt die Erzeugung von oxidativem Stress eine Rolle.[3][6][7][8] In niedrigen Konzentrationen scheint Salsolinol neuroprotektive Eigenschaften zu haben.[9] Salsolinol ist ein Metabolit des Ethanols und als solcher für dessen berauschende Wirkung mitverantwortlich.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
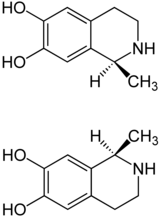 | ||||||||||
| 1:1-Gemisch aus (S)-Form (oben) und (R)-Form (unten) | ||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||
| Name | Salsolinol | |||||||||
| Andere Namen |
1-Methyl-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisochinolin (IUPAC) | |||||||||
| Summenformel |
| |||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
grauer Feststoff[1] | |||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 179,22 g·mol−1 [Salsolinol] | |||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | |||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
sehr gering in Wasser[1] | |||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||
Bedeutung als Ethanolmetabolit
Im Organismus bildet sich nach Ethanolaufnahme Salsolinol aus Acetaldehyd, d. h. dem ersten metabolischen Oxidationsprodukt des Ethanols, und dem Neurotransmitter Dopamin.[10]
Beide Enantiomere des Salsolinols sind funktionell selektive Agonisten am μ-Opioidrezeptor, indem sie den Signalpfad über das G-Protein aktivieren, nicht hingegen über das β-Arrestin. Die Potenz des Razemats ist mit EC50 von 20 μM deutlich schwächer als die von Morphin (4 nM). (S)-Salsolinol ist wirksamer als sein Pendant (EC50 = 9 μM versus 600 μM). Am Rezeptor besetzen Morphin und Salsolinol dieselbe Bindungsstelle und nehmen dabei die gleiche Lage ein.[11]
Synthese
Salsolinol wird biochemisch aus Dopamin und Pyruvat synthetisiert. Katalysiert wird die biochemische Synthese durch das Enzym Salsolinol-Synthase. Dabei entsteht (R)-(+)-Salsolinol.
Sowohl physiologisch als auch präparativ (z. B. im Labor) bildet sich razemisches (RS)-Salsolinol durch Kondensation von Dopamin mit Acetaldehyd gemäß der Pictet-Spengler-Reaktion.
Stereoisomerie
Salsolinol ist chiral und enthält ein Stereozentrum. Es existieren also zwei Enantiomere, das (S)-Salsolinol und das (R)-Salsolinol. Die Enantiomere besitzen unterschiedliche Cytotoxizität: (S)-Salsolinol ist zytotoxischer (IC50 = 67 μmol·l−1) als (R)-Salsolinol (IC50 = 167 μmol·l−1).[12]
Einzelnachweise
- Datenblatt Salsolinol bei Acros, abgerufen am 19. Februar 2010.
- Datenblatt 1-Methyl-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydrobromide bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 9. Mai 2017 (PDF).
- M. F. Melzig, I. Putscher, P. Henklein, H. Haber: In vitro pharmacological activity of the tetrahydroisoquinoline salsolinol present in products from Theobroma cacao L. like cocoa and chocolate, in: Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2000, 73, S. 153–159. doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00291-9.
- Eintrag zu (R)-Salsolinol in der Human Metabolome Database (HMDB), abgerufen am 25. September 2013.
- Naoi M, Maruyama W, Akao Y, Zhang J, Parvez H: Apoptosis induced by an endogenous neurotoxin, N-methyl(R)salsolinol, in dopamine neurons. In: Toxicology. 153, Nr. 1–3, 2000, S. 123–41. PMID 11090952.
- J. H. Kang: Salsolinol, a tetrahydroisoquinoline catechol neurotoxin, induces human Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase modification, in: J. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2007, 40 (5), S. 684–689. PMID 17927901.
- Kim SS, Kang JY, Kang JH: Oxidative modification of human ceruloplasmin induced by a catechol neurotoxin, salsolinol. In: BMB Rep. 49, Nr. 1, 2016, S. 45–50. PMID 26077029. PMC 4914212 (freier Volltext).
- Kang JH: Salsolinol, a catechol neurotoxin, induces oxidative modification of cytochrome c. In: BMB Rep. 46, Nr. 2, 2013, S. 119–23. PMID 23433116. PMC 4133855 (freier Volltext).
- Możdżeń E, Kajta M, Wąsik A, Lenda T, Antkiewicz-Michaluk L: Salsolinol, an endogenous compound triggers a two-phase opposing action in the central nervous system. In: Neurotox Res. 27, Nr. 3, 2015, S. 300–13. doi:10.1007/s12640-014-9511-y. PMID 25537852. PMC 4353863 (freier Volltext).
- Deehan GA, Brodie MS, Rodd ZA: What is in that drink: the biological actions of ethanol, acetaldehyde, and salsolinol. In: Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 13, 2013, S. 163–84. doi:10.1007/7854_2011_198. PMID 22351424. PMC 4955731 (freier Volltext).
- Berríos-Cárcamo P, Quintanilla ME, Herrera-Marschitz M, Vasiliou V, Zapata-Torres G, Rivera-Meza M: Racemic Salsolinol and its Enantiomers Act as Agonists of the μ-Opioid Receptor by Activating the Gi Protein-Adenylate Cyclase Pathway. In: Front Behav Neurosci. 10, 2016, S. 253. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00253. PMID 28167903.
- M. F. Melzig, I. Putscher, H. Haber, M. Rottmann und J. Zipper: Toxicity and Pharmacological Effects of Salsolinol in Different Cultivated Cells in A. Moser: Pharmacology of Endogenous Neurotoxins, Birkhäuser Verlag Boston (1998), ISBN 978-0-8176-3993-8, S. 253.
