Reitgräser
Reitgräser (Calamagrostis) sind eine Pflanzengattung innerhalb der Familie der Süßgräser (Poaceae). Die etwa 230 Arten sind fast weltweit verbreitet. Der deutsche Trivialname Reitgras, auch Reutgras bedeutet so viel wie „Rodungsgras“ und bezieht sich auf Calamagrostis epigejos, das jedoch nicht auf Rodungen, sondern auf Waldschlägen wächst.[1]
| Reitgräser | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
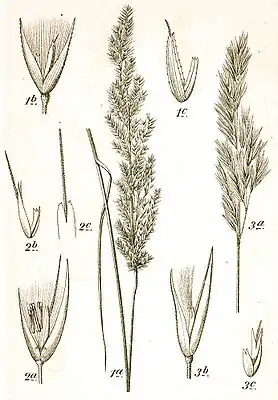
1. Sumpf-Reitgras (Calamagrostis canescens), 2. Ufer-Reitgras (Calamagrostis pseudophragmites) und 3. Land-Reitgras (Calamagrostis epigejos), Kupferstich von Jacob Sturm | ||||||||||||
| Systematik | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Wissenschaftlicher Name | ||||||||||||
| Calamagrostis | ||||||||||||
| Adans. |
Beschreibung
Vegetative Merkmale
Die Reitgras-Arten sind ausdauernde krautige Pflanzen. Es sind horstbildende Gräser, die häufig unterirdische Ausläufer bilden. Die zahlreichen Erneuerungstriebe wachsen innerhalb oder außerhalb der unteren Blattscheiden (intra- oder extravaginal) hoch. Die Halme sind einfach oder an den unteren Knoten verzweigt und besitzen mehrere Knoten.
Die wechselständig am Halm angeordneten Laubblätter sind in Blattscheide und Blattspreite gegliedert. Die Blattscheiden sind bis zum Grund offen, gerieft, manchmal behaart und glatt oder rau. Das Blatthäutchen ist ein häutiger Saum. Die einfachen Blattspreiten sind lang und 1,5 bis 12 Millimeter breit. Sie sind flach, gerippt. Auf den Rippen sind sie rau, kahl bis behaart. Der Blattrand ist rau und häufig schneidend.
Generative Merkmale
Der rispige Blütenstand ist reich verzweigt, meist aufrecht und nur zur Anthese ausgebreitet. Die Ährchen bestehen aus einem zwittrigen Blütchen und sind 3 bis 8 Millimeter lang, schmal und seitlich zusammengedrückt. Das Blütchen trägt am Grund der Deckspelze längere Haare, die meist gleich lang wie oder länger als die Deckspelze sind. Die Blüte fällt zur Fruchtreife als Ganzes aus den Hüllspelzen aus. Die Ährchenachse trägt an den Kanten lange weiße Haare. Die zwei Hüllspelzen sind ein- bis dreinervig und so lang wie das Ährchen. Sie sind spitz bis zugespitzt, häutig und ungleich, wobei das untere länger als das obere ist. Die Deckspelze ist drei- oder fünfnervig und halb bis 3/4 so lang wie die Hüllspelzen. Sie ist spitz oder hat zwei kurze Seitenlappen, ist häutig, kahl und trägt eine Granne. Diese sitzt meistens auf dem Rücken der Spelze, selten zwischen den Seitenlappen oder an der Spitze. Die Vorspelze hat zwei Nerven, ist bis zu gleich lang wie die Deckspelze, zarthäutig und kahl. Es gibt drei Staubblätter. Der Fruchtknoten ist kahl und trägt zwei endständige Griffel mit kurzen, federigen Narben.
Die Karyopse ist kahl. Der Nabel ist länglich und nimmt bis zu einem Viertel der Fruchtlänge ein.
Chromosomensätze
Die Chromosomengrundzahl beträgt x = 7. Die Calamagrostis-Arten sind tetraploid oder haben einen noch höheren Ploidiegrad.
Fortpflanzung
Bei den tetraploiden Calamagrostis-Arten verläuft die Meiose normal, sie sind Fremdbefruchter. Bei Sippen mit höherer Ploidie kommt es häufig zu Störungen in der Meiose, sie pflanzen sich teilweise apomiktisch fort. Das Verhältnis zwischen apomiktischer und sexueller Samenbildung kann dabei je nach Alter der Pflanze und nach Jahreszeit variieren. Einige Arten, wie Calamagrostis purpurea und Calamagrostis pseudopurpurea pflanzen sich rein apomiktisch fort.
Wenn zwei Arten im gleichen Gebiet vorkommen, bilden sie häufig Hybride, die stets steril sind, sich aber vegetativ vermehren können.
Systematik und Verbreitung
Die Gattung Calamagrostis wurde 1763 durch Michel Adanson aufgestellt. Der Gattungsname Calamagrostis leitet sich von den griechischen Wörtern kalamagrostis für „Rohrgras, Schilfgras“ ab, zu kalamos für „Rohr“ und agrostis für „Futtergras“ ab. Synonyme für Calamagrostis Adans. sind: Ancistrochloa Honda, Anisachne Keng, Athernotus Dulac, Chamaecalamus Meyen, Cinnagrostis Griseb., Deyeuxia Clarion ex P.Beauv., Sclerodeyeuxia Pilg., Stilpnophleum Nevski, Stylagrostis Mez.[2] Über den Umfang der Gattung Calamagrostis und die Abgrenzung oder Einbeziehung der Gattungen Agrostis sowie Deyeuxia wird kontrovers diskutiert.[3]
Die Gattung Calamagrostis ist weltweit verbreitet. Ein Mannigfaltigkeitszentrum liegt mit rund 100 Arten in Südamerika.[4] In der Gattung Calamagrostis s. l. etwa 230 Arten, von denen nach Fischer 2008 14 in Europa vorkommen.[1] In Mitteleuropa kommen acht bis neun Arten vor: Wald-Reitgras (Calamagrostis arundinacea), Sumpf-Reitgras (Calamagrostis canescens), Land-Reitgras (Calamagrostis epigejos), Ufer-Reitgras (Calamagrostis pseudophragmites), Purpur-Reitgras (Calamagrostis purpurea), Sächsisches Reitgras (Calamagrostis rivalis), Moor-Reitgras (Calamagrostis stricta), Berg-Reitgras (Calamagrostis varia), Wolliges Reitgras (Calamagrostis villosa).[1]
Die Gattung Calamagrostis wird in die Tribus Aveneae oder auch Poeae in der Unterfamilie Pooideae innerhalb der Familie der Poaceae gestellt. Es gibt viele Naturhybriden.
.jpg.webp)





In der Gattung Calamagrostis s. l. gibt etwa 230 Arten:[2]
- Calamagrostis abnormis (Hook. f.) U.Shukla[2]
- Calamagrostis acuminata (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis ×acutiflora (Schrad.) DC.[2]
- Calamagrostis affinis (M.Gray) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis ajanensis Kharkev. & Prob.[2]
- Calamagrostis alajica Litv.[2]
- Calamagrostis alba (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis albiflora Vaniot[2]
- Calamagrostis altaica Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis amoena (Pilg.) Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis ampliflora Tovar[2]
- Calamagrostis ×andrejewii Litv.[2]
- Calamagrostis angustifolia Kom.[2]
- Calamagrostis anthoxanthoides (Munro) Regel[2]
- Calamagrostis appressa (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis archboldii Hitchc.[2]
- Wald-Reitgras (Calamagrostis arundinacea (L.) Roth) (Syn.:Calamagrostis brachytricha Steud.): Es ist in den gemäßigte Gebieten Eurasiens und in Neuguinea weitverbreitet.[2]
- Calamagrostis atjehensis Ohwi[2]
- Calamagrostis aurea (Munro) Hack. ex Sodiro[2]
- Calamagrostis australis (Moritzi) Buse[2]
- Calamagrostis austrodensa Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis austroscaberula Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis autumnalis Koidz.[2]
- Calamagrostis avenoides (Hook. f.) Cockayne[2]
- Calamagrostis ×badzhalensis Prob.[2]
- Calamagrostis balkharica P.A.Smirn.[2]
- Calamagrostis benthamiana (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis ×bihariensis Simonk.[2]
- Calamagrostis bogotensis (Pilg.) Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis bolanderi Thurb.[2]
- Calamagrostis boliviensis Hack.[2]
- Calamagrostis borii Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis boyacensis Swallen & Garc.-Barr.[2]
- Calamagrostis brachyathera (Stapf) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis brassii Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis breviaristata (Wedd.) Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis brevifolia (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis breweri Thurb.[2]
- Calamagrostis cabrerae Parodi[2]
- Calamagrostis cainii Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis calderillensis Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis canadensis (Michx.) P.Beauv.[2]
- Sumpf-Reitgras (Calamagrostis canescens (Weber) Roth): Es ist von Europa bis zur Türkei und Sibirien weitverbreitet.[2]
- Calamagrostis carchiensis Laegaard[2]
- Calamagrostis carinata (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis caucasica Trin.[2]
- Calamagrostis cephalantha Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis chalybaea (Laest.) Fr.[2]
- Calamagrostis chaseae Luces[2]
- Calamagrostis chilensis Phil.[2]
- Calamagrostis chrysantha (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis chrysophylla (Phil.) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis cleefii Escalona[2]
- Calamagrostis clipeata Vaniot[2]
- Calamagrostis coahuilensis P.M.Peterson, Soreng & Valde´s-Reyna[2]
- Calamagrostis coarctata Eaton[2]
- Calamagrostis conferta (Keng) P.C.Kuo & S.L.Lu[2]
- Calamagrostis ×conwentzii Ulbr.[2]
- Calamagrostis cordechii Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis crassiuscula (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis crispa (Rugolo & Villav.) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis cryptolopha (Wedd.) Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis curta (Wedd.) Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis curtoides (Rugolo & Villav.) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis curvula (Wedd.) Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis cuzcoensis Tovar[2]
- Calamagrostis ×czerepanovii Husseinov[2]
- Calamagrostis debilis Hook. f.[2]
- Calamagrostis decipiens (R.Br.) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis decora Hook. f.[2]
- Calamagrostis densiflora (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis deschampsiiformis C.E.Hubb.[2]
- Calamagrostis deschampsioides Trin.[2]
- Calamagrostis deserticola (Phil.) Phil.[2]
- Calamagrostis diemii (Rúgolo) Soreng[2]
- Calamagrostis diffusa (Keng) Keng f.[2]
- Calamagrostis divaricata P.M.Peterson & Soreng[2]
- Calamagrostis divergens Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis dmitrievae Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis drummondii (Steud.) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis ecuadoriensis Laegaard[2]
- Calamagrostis effusa (Kunth) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis effusiflora (Rendle) P.C.Kuo & S.L.Lu ex J.L.Yang[2]
- Calamagrostis elatior (Griseb.) A.Camus[2]
- Calamagrostis eminens (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis emodensis Griseb.: Sie ist vom nördlichen Indien über Kaschmir, nördlichen Pakistan, Bhutan, Tibet bis zu den chinesischen Provinzen Shaanxi, Sichuan sowie Yunnan verbreitet.[3]
- Land-Reitgras (Calamagrostis epigejos (L.) Roth): Es ist in den gemäßigte Gebieten Eurasiens weitverbreitet. Sie ist in Nordamerika ein Neophyt. Sie kommt in einer besonderen Unterart in Afrika vor.[2]
- Calamagrostis erectifolia Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis eriantha (Kunth) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis expansa (Munro ex Hillebr.) Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis fauriei Hack.[2]
- Calamagrostis fibrovaginata Laegaard[2]
- Calamagrostis fiebrigii Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis filifolia Merr.[2]
- Calamagrostis filipes (Keng) P.C.Kuo & S.L.Lu ex J.L.Yang[2]
- Calamagrostis flaccida Keng f.[2]
- Calamagrostis foliosa Kearney[2]
- Calamagrostis frigida (Benth.) Maiden & Betche[2]
- Calamagrostis fulgida Laegaard[2]
- Calamagrostis fulva (Griseb.) Kuntze[2]
- Calamagrostis fuscata (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis gayana (Steud.) Soreng[2]
- Calamagrostis gigas Takeda[2]
- Calamagrostis glacialis (Wedd.) Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis griffithii (Bor) G.Singh[2]
- Calamagrostis guamanensis Escalona[2]
- Calamagrostis guatemalensis Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis gunniana (Nees) Reeder[2]
- Calamagrostis hackelii Lillo ex Stuck.[2]
- Calamagrostis hakonensis Franch. & Sav.[2]
- Calamagrostis × hartmaniana Fr.[2]
- Calamagrostis × haussknechtiana Torges[2]
- Calamagrostis hedbergii Melderis[2]
- Calamagrostis henryi (Rendle) P.C.Kuo & S.L.Lu ex J.L.Yang[2]
- Calamagrostis heterophylla (Wedd.) Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis hedinii Pilg. ex Hedin: Sie ist vom nordwestlichen Indien über Kaschmir, Pakistan, Kirgisistan, Tadschikistan, Tibet, Xinjiang bis zu den chinesischen Provinzen Qinghai sowie Sichuan verbreitet[3]
- Calamagrostis hieronymi Hack.[2]
- Calamagrostis hillebrandii (Munro ex Hillebr.) C.L.Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis hirta (Sodiro ex Mille) Laegaard[2]
- Calamagrostis holciformis Jaub. & Spach[2]
- Calamagrostis holmii Lange[2]
- Calamagrostis howellii Vasey[2]
- Calamagrostis hupehensis (Rendle) Chase[2]
- Calamagrostis imbricata (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis inaequalis (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis inexpansa A.Gray[2]
- Calamagrostis insperata Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis intermedia (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis involuta Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis jamesonii Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis kalarica Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis kengii T.F.Wang: Sie gedeiht im Wald, am Waldrand, feuchten Standorten und auf Ödland nur in den chinesischen Provinzen Heilongjiang sowie Jilin.[3]
- Calamagrostis killipii Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis koelerioides Vasey[2]
- Calamagrostis kokonorica Keng ex Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis korotkyi Litv.[2]
- Calamagrostis korshinskyi Litv.[2]
- Calamagrostis ×kotulae Zapal.[2]
- Calamagrostis ×kuznetzovii Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis lahulensis G.Singh[2]
- Calamagrostis lapponica (Wahlenb.) Hartm.[2]
- Calamagrostis lawrencei (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis leiophylla (Wedd.) Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis leonardii Chase[2]
- Calamagrostis levipes (Keng) P.C.Kuo & S.L.Lu ex J.L.Yang[2]
- Calamagrostis licentiana Hand.-Mazz.[2]
- Calamagrostis ligulata (Kunth) Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis linifolia Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis llanganatensis Laegaard[2]
- Calamagrostis longiseta Hack.[2]
- Calamagrostis macbridei Tovar[2]
- Calamagrostis macilenta (Griseb.) Litv.[2]
- Calamagrostis macrophylla (Pilg.) Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis malamalensis Hack. ex Stuck.[2]
- Calamagrostis mandoniana (Wedd.) Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis matsumurae Maxim.[2]
- Calamagrostis mckiei (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis menhoferi Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis meridensis (Luces) Briceño[2]
- Calamagrostis mesathera (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis microseta (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis minarovii Hüseyin[2]
- Calamagrostis minima (Pilg.) Tovar[2]
- Calamagrostis minor (Benth.) J.M.Black[2]
- Calamagrostis mollis Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis montanensis (Scribn.) Scribn. ex Vasey[2]
- Calamagrostis moupinensis Franch.[2]
- Calamagrostis muiriana B.L.Wilson & Sami Gray[2]
- Calamagrostis mulleri Luces[2]
- Calamagrostis munroi Boiss.[2]
- Calamagrostis nagarum (Bor) G.Singh[2]
- Calamagrostis nardifolia (Griseb.) Hack. ex Stuck.[2]
- Calamagrostis neesii Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis neocontracta Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis niitakayamensis Honda[2]
- Calamagrostis ningxiaensis D.Z.Ma & J.N.Li[2]
- Calamagrostis nitidula Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis nivicola (Hook. f.) Hand.-Mazz.[2]
- Calamagrostis nudiflora (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis nutkaensis (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis obtusata Trin.[2]
- Calamagrostis ophitidis (Howell) Nygren[2]
- Calamagrostis orbignyana (Wedd.) Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis orizabae (Rupr. ex E.Fourn.) Beal[2]
- Calamagrostis ovata (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis ×paradoxa Lipsky[2]
- Calamagrostis parsana (Bor) M.Dogan[2]
- Calamagrostis parviseta (Vickery) Reeder[2]
- Calamagrostis patagonica (Speg.) Makloskie[2]
- Calamagrostis pavlovii (Roshev.) Roshev.[2]
- Calamagrostis perplexa Scribn.[2]
- Calamagrostis petelotii (Hitchc.) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis pickeringii A.Gray[2]
- Calamagrostis pinetorum Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis pisinna Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis pittieri Hack.[2]
- Calamagrostis planifolia (Kunth) Trin. ex Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis poluninii T.J.Sørensen[2]
- Calamagrostis polycephala Vaniot[2]
- Calamagrostis polygama (Griseb.) Parodi[2]
- Calamagrostis ×ponojensis Montell[2]
- Calamagrostis porteri A.Gray[2]
- Calamagrostis ×prahliana Torges[2]
- Calamagrostis preslii (Kunth) Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis pringlei Beal[2]
- Calamagrostis przevalskyi Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis ×pseudodeschampsioides Tzvelev[2]
- Ufer-Reitgras (Calamagrostis pseudophragmites (Haller f.) Koeler): Es ist von Europa bis Japan und zum Himalaja verbreitet.[2]
- Calamagrostis pungens Tovar[2]
- Calamagrostis purpurascens R.Br.[2]
- Purpur-Reitgras (Calamagrostis purpurea (Trin.) Trin., Syn.:Calamagrostis phragmitoides Hartm.): Es ist in subarktischen und subalpinen Gebieten der Nordhalbkugel verbreitet.[2]
- Calamagrostis pusilla Reeder[2]
- Calamagrostis quadriseta (Labill.) Spreng.[2]
- Calamagrostis radicans Vaniot[2]
- Calamagrostis ramonae Escalona[2]
- Calamagrostis rauhii Tovar[2]
- Calamagrostis recta (Kunth) Trin. ex Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis reflexa (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis reitzii Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis ×rigens Lindgr.[2]
- Calamagrostis rigescens (J.Presl) Scribn.[2]
- Calamagrostis rigida (Kunth) Trin. ex Steud.[2]
- Sächsisches Reitgras (Calamagrostis rivalis (Torges) H.Scholz,[5] Syn.: Calamagrostis pseudopurpurea Gerstl. ex O.R. Heine): Dieser Endemit kommt nur in Sachsen und Sachsen-Anhalt vor. Wird von manchen Autoren aber als Synonym zu Calamagrostis purpurea (Trin.) Trin. gestellt.[2]
- Calamagrostis rodwayi (Vickery) Govaerts[2]
- Calamagrostis rosea (Griseb.) Hack.[2]
- Calamagrostis rubescens Buckley[2]
- Calamagrostis rupestris Trin.[2]
- Calamagrostis sachalinensis F.Schmidt[2]
- Calamagrostis sajanensis Malyschev[2]
- Calamagrostis salina Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis scaberula Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis scabrescens Griseb. (Syn.: Deyeuxia scabrescens (Griseb.) Munro ex Duthie, Deyeuxia dispar L.Liu, Deyeuxia sikangensis Keng, Deyeuxia simlensis Bor, Calamagrostis scabrescens var. humilis Griseb., Calamagrostis simlensis (Bor) G.Singh, Calamagrostis sikangensis (Keng) P.C.Kuo & S.L.Lu ex J.L.Yang)[2]
- Calamagrostis scabriflora Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis schmidtiana Tzvelev & Prob.: Sie wurde 2010 aus Sachalin erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Calamagrostis sclerantha Hack.[2]
- Calamagrostis sclerophylla (Stapf) Hitchc.[2]
- Calamagrostis scopulorum M.E.Jones[2]
- Calamagrostis scotica (Druce) Druce[2]
- Calamagrostis sesquiflora (Trin.) Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis setiflora (Wedd.) Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis sichuanensis J.L.Yang[2]
- Calamagrostis sichotensis Tzvelev & Prob.: Sie wurde 2010 aus Russlands Fernen Osten erstbeschrieben.[2]
- Calamagrostis sinelatior (Keng) P.C.Kuo & S.L.Lu ex J.L.Yang (Syn.: Deyeuxia sinelatior Keng)[2]: Sie gedeiht im Wald und am Waldrand in Höhenlagen von 1000 bis 3200 Metern in den chinesischen Provinzen Henan, Shaanxi sowie Sichuan.[3]
- Calamagrostis smirnowii Litv. ex Petrov[2]
- Calamagrostis spicigera (J.Presl) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis spruceana (Wedd.) Hack. ex Sodiro[2]
- Calamagrostis srilankensis Davidse[2]
- Calamagrostis staintonii G.Singh[2]
- Calamagrostis stenophylla Hand.-Mazz.[2]
- Calamagrostis steyermarkii Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis stolizkai Hook. f.[2]
- Moor-Reitgras (Calamagrostis stricta (Timm) Koeler): Es ist in subarktischen bis gemäßigten Gebieten der Nordhalbkugel verbreitet und kommt von Peru bis zum südlichen Südamerika vor.[2]
- Calamagrostis ×strigosa (Wahlenb.) Hartm.[2]
- Calamagrostis subacrochaet Nakai[2]
- Calamagrostis ×subchalybaea Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis ×subepigeios Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis sublanceolata Honda[2]
- Calamagrostis ×submonticola Prob.[2]
- Calamagrostis ×subneglecta Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis suka Speg.[2]
- Calamagrostis tacomensis K.L.Marr & Hebda[2]
- Calamagrostis tarmensis Pilg.[2]
- Calamagrostis tashiroi Ohwi[2]
- Calamagrostis ×tatianae Prob.[2]
- Calamagrostis teberdensis Litv.[2]
- Calamagrostis teretifolia Laegaard[2]
- Calamagrostis tianschanica Rupr.[2]
- Calamagrostis tibetica (Bor) Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis tolucensis (Kunth) Trin. ex Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis ×torgesiana Hausskn.[2]
- Calamagrostis trichodonta (Wedd.) Soreng[2]
- Calamagrostis turkestanica Hack.[2]
- Calamagrostis tweedyi (Scribn.) Scribn.[2]
- Calamagrostis tzvelevii Hüseyin[2]
- Calamagrostis ×uralensis Litv.[2]
- Calamagrostis ×ussuriensis Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis valida Sohns[2]
- Berg-Reitgras (Calamagrostis varia (Schrad.) Host): Es kommt in Europa vor.[2]
- Calamagrostis ×vassiljevii Tzvelev[2]
- Calamagrostis velutina (Nees & Meyen) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis veresczaginii Zolot.[2]
- Calamagrostis vicunarum (Wedd.) Pilg.[2]
- Wolliges Reitgras (Calamagrostis villosa (Chaix) J.F.Gmel.): Es kommt von Frankreich bis zur Ukraine vor.[2]
- Calamagrostis violacea (Wedd.) Hack.[2]
- Calamagrostis viridiflavescens (Poir.) Steud.[2]
- Calamagrostis viridis (Phil.) Soreng[2]
- Calamagrostis vulcanica Swallen[2]
- Calamagrostis yanyuanensis J.L.Yang[2]
- Calamagrostis ×yatabei Maxim.[2]
- Calamagrostis youngii (Hook. f.) Buchanan[2]
- Calamagrostis zenkeri (Trin.) Davidse[2]
- Calamagrostis ×zerninensis Lüderw.[2]
Literatur
- Siegmund Seybold (Hrsg.): Schmeil-Fitschen interaktiv. CD-ROM, Version 1.1. Quelle & Meyer, Wiebelsheim 2002, ISBN 3-494-01327-6.
- Walter Erhardt, Erich Götz, Nils Bödeker, Siegmund Seybold: Der große Zander. Enzyklopädie der Pflanzennamen. Band 2. Arten und Sorten. Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart (Hohenheim) 2008, ISBN 978-3-8001-5406-7.
- Hans Joachim Conert: Calamagrostis. In: Hans Joachim Conert (Hrsg.): Illustrierte Flora von Mitteleuropa. Begründet von Gustav Hegi. 3., völlig neubearbeitete Auflage. Band I. Teil 3: Spermatophyta: Angiospermae: Monocotyledones 1(2). Poaceae (Echte Gräser oder Süßgräser). Parey Buchverlag, Berlin 1998, ISBN 3-8263-2868-X, S. 357–380 (erschienen in Lieferungen 1979–1998 5. Lieferung, 1989).
Einzelnachweise
- Manfred A. Fischer, Karl Oswald, Wolfgang Adler: Exkursionsflora für Österreich, Liechtenstein und Südtirol. 3., verbesserte Auflage. Land Oberösterreich, Biologiezentrum der Oberösterreichischen Landesmuseen, Linz 2008, ISBN 978-3-85474-187-9.
- Rafaël Govaerts, 2011: World checklist of selected plant families published update. Facilitated by the Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Rafaël Govaerts (Hrsg.): Calamagrostis. In: World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) – The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- Sheng-lian Lu, Sylvia M. Phillips: In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (Hrsg.): Flora of China. Volume 22: Poaceae, Science Press und Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing und St. Louis 2006, ISBN 1-930723-50-4.Calamagrostis s. str., S. 359–360 - textgleich online wie gedrucktes Werk.
- Calamagrostis, In: W. D. Clayton, K. T Harman, H. Williamson: GrassBase - The Online World Grass Flora. 2006 ff., abgerufen 19. Juli 2008.
- Thomas Raus, Hildemar Scholz: Once again: The correct name of the endemic Calamagrostis from Saxony (Germany). In: Feddes Repertorium. Band 113, Nr. 3–4, 2002, S. 271–272, doi:10.1002/1522-239X(200208)113:3/4<271::AID-FEDR271>3.0.CO;2-N.