N-(Cyclohexylthio)phthalimid
N-(Cyclohexylthio)phthalimid ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Carbonsäureimide und Sulfenamide.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
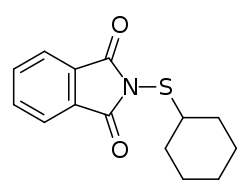 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | N-(Cyclohexylthio)phthalimid | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C14H15NO2S | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
beiger Feststoff mit schwachem Geruch[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 261,33 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
1,354 g·cm−3[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
400 °C[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||||||||
Gewinnung und Darstellung
N-(Cyclohexylthio)phthalimid kann durch Reaktion von Cyclohexylsulfenylchlorid (welches wiederum aus Cyclohexanthiol gewonnen wird) mit Phthalimid gewonnen werden.[3]
Eigenschaften
N-(Cyclohexylthio)phthalimid ist ein brennbarer, schwer entzündbarer, beiger Feststoff mit schwachem Geruch, der praktisch unlöslich in Wasser ist.[1] Das technische Produkt ist ein weißer, gelbbrauner oder rosafarbener, charakteristisch unangenehm riechender Feststoff, der sich ab 150 °C beginnt zu zersetzen.[2]
Verwendung
N-(Cyclohexylthio)phthalimid wird als Vulkanisationsverzögerer in der Gummiindustrie verwendet.[4]
Sicherheitshinweise
N-(Cyclohexylthio)phthalimid ist ein Typ IV-Kontaktallergen.[5][6]
Einzelnachweise
- Eintrag zu N-(Cyclohexylthio)phthalimid in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 20. Januar 2022. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- Gefahrstoffinformationssystem Chemikalien der BG RCI und der BGHM: N-(Cyclohexylthio)phthalimid (CTP) (17796-82-6): Charakterisierung, Grenzwerte, Einstufungen, abgerufen am 27. Januar 2019
- European Patent Office: EP 0775695 A1 19970528 - Process for the preparation of N-cyclohexylthiophthalimide, abgerufen am 27. Januar 2019
- Michael H. S. Gradwell, Nigel R. Stephenson: The Action of N-(Cyclohexylthio)Phthalimide as a Prevulcanization Inhibitor of 2-Bisbenzothiazole-2,2′-Disulfide Accelerated Sulfur Vulcanization . In: Rubber Chemistry and Technology. 74, 2001, S. 44, doi:10.5254/1.3547638.
- alles-zur-allergologie.de: Allergen Cyclohexylthiophthalimid (CTP), abgerufen am 27. Januar 2019.
- S. Huygens, A. Barbaud, A. Goossens: Frequency and relevance of positive patch tests to cyclohexylthiophthalimide, a new rubber allergen. In: Eur J Dermatol. 11, S. 443–445, PMID 11525953.

