Propylhexedrin
Propylhexedrin (auch Hexahydrodesoxyephedrin) ist ein zentralnervöses Stimulans, das in den USA als Benzedrex Inhalierstift vermarktet wird. Propylhexedrin ist strukturverwandt mit Methamphetamin.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
-Propylhexedrin_Enantiomers_Structural_Formulae.png.webp) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (R)-Isomer (links) und (S)-Isomer (rechts) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Freiname | Propylhexedrin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C10H21N | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arzneistoffangaben | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wirkstoffklasse | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 155,28 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| pKS-Wert |
4,78 (pKb)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
schwer löslich in Wasser, mischbar mit Ethanol, Chloroform und Diethylether[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxikologische Daten | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Es wird vor allem zur symptomatischen Behandlung von Nasenausfluss bei Erkältungen und Allergien angewendet.
Das auch als Levopropylhexedrin bezeichnete (S)-Enantiomer[7] wird auch als Appetitzügler verwendet.[2] Das Salz des (S)-Enantiomers mit Phenobarbital ergibt den antiepileptisch wirkenden Arzneistoff Barbexaclon.
Synthese
Propylhexedrin kann durch die Kernhydrierung von Methamphetamin in Gegenwart von Platin(IV)-oxid als Katalysator hergestellt werden:[8]
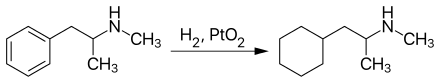
Eine Enantiomerentrennung kann mit Hilfe von L-(+)-Weinsäure erfolgen.[9]
Einzelnachweise
- The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 14. Auflage. Merck & Co., Whitehouse Station NJ 2006, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1, S. 1350–1351.
- Eintrag zu Levopropylhexedrin. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 15. November 2014.
- L. G. Chatten, L. E. Harris: Relationship between pKb(H2O) of Organic Compounds and E 1∕2 Values in Several Nonaqueous Solvents., in: Anal. Chem. 1962, 34, 1495–1501; doi:10.1021/ac60191a041.
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- A. Kleemann, J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances – Synthesis, Patents, Applications, 4th Edition, Thieme 2001, ISBN 3-13-115134-X.
- Lands, A.M.; Nash, V.L.; Granger, H.R.; Dertinger, B.L.: The Pharmacologic Activity of N-Methyl-β-cyclohexylisopropylamine Hydrochloride in J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.89 (1947) 382–385.
- Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu Levopropylhexedrin: CAS-Nummer: 6192-97-8, EG-Nummer: 228-245-0, ECHA-InfoCard: 100.025.678, PubChem: 71197, ChemSpider: 64333, Wikidata: Q15409406.
- B.L. Zenitz, E.B. Macks, M.L. Moore: Preparation of Some Primary and Secondary β-Cyclohexylalkylamines in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 69 (1947) 1117-1121. doi:10.1021/ja01197a039
- Patent US2454746: Cyclohexylalkylamines. Angemeldet am 13. Mai 1947, veröffentlicht am 23. November 1948, Anmelder: Smith, Kline & French Labor, Erfinder: Glenn E. Ullyot.