Cyclohexylmethanol
Cyclohexylmethanol ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Klasse der Cycloalkane und der Alkohole.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
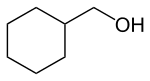 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Cyclohexylmethanol | ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C7H14O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
gelbliche Flüssigkeit mit Geruch nach Alkohol[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 114,19 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
0,9339 g·cm−3[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt |
19 °C[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
187–188 °C[3] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
gering in Wasser[4] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,4640[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Toxikologische Daten |
910 μmol·L−1 (EC50, Rana Pipiens, transdermal)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | |||||||||||||||||||
Eigenschaften
Cyclohexylmethanol besitzt einen Flammpunkt von 71 °C.[1]
Herstellung
Cyclohexylmethanol kann durch Hydroformylierung aus Cyclohexen hergestellt werden. Als Nebenprodukt entsteht durch Hydrierung auch Cyclohexan.[7]
Einzelnachweise
- Eintrag zu Cyclohexylmethanol in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 4. Oktober 2014. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- Vinzenz Prey, Jürgen Bartsch: Dipolmessungen an Pyranose- und Furanose-Modellsubstanzen. In: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 712, 1968, S. 201–207, doi:10.1002/jlac.19687120124.
- Bruce Rickborn, Stanley E. Wood: Cleavage of cyclopropanes by diborane. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 93, 1971, S. 3940–3946, doi:10.1021/ja00745a021.
- Paul Ruelle, Ulrich W. Kesselring: The hydrophobic propensity of water toward amphiprotic solutes: Predicton and molecular origin of the aqueous solubility of aliphatic alcohols. In: Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 86, 1997, S. 179–186, doi:10.1021/js9603109.
- Datenblatt Cyclohexanemethanol bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 25. Mai 2017 (PDF).
- D. E. Raines, S. E. Korten, A. G. Hill, K. W. Miller: Anesthetic cutoff in cycloalkanemethanols. A test of current theories. In: Anesthesiology. Band 78, Nummer 5, Mai 1993, S. 918–927, PMID 8489064.
- Patent EP2000453: METHOD FOR PRODUCING ALCOHOL BY USING CARBON DIOXIDE AS RAW MATERIAL. Veröffentlicht am 10. Dezember 2008, Erfinder: TOMINAGA KENICHI.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.