Boyland-Sims-Oxidation
Die Boyland-Sims-Oxidation ist eine Namensreaktion aus dem Bereich der organischen Chemie und wurde das erste Mal 1953 von Eric Boyland (1905–2002) und Peter Sims (1919–1983) beobachtet. Dabei reagieren Aniline mit alkalischem Kaliumperoxodisulfat zu ortho-Aminophenolen.[1]
Übersichtsreaktion
Die Boyland-Sims-Oxidation wird in basischer, wässriger Lösung ausgeführt (R1, R2 = Alkylgruppe oder Wasserstoff):

Die blau eingezeichnete phenolische OH-Gruppe in ortho-Position ist durch die Boyland-Sims-Oxidation eingeführt worden. Sind beide ortho-Positionen im Edukt besetzt, bildet sich ein para-Aminophenol.
Möglicher Mechanismus
Der folgende Mechanismus der Boyland-Sims-Oxidation wird in einer wässrigen Kaliumhydroxid-Lösung durch einen ipso-Angriff der Peroxidgruppe des Kaliumperoxodisulfats an Anilin erklärt.[2]
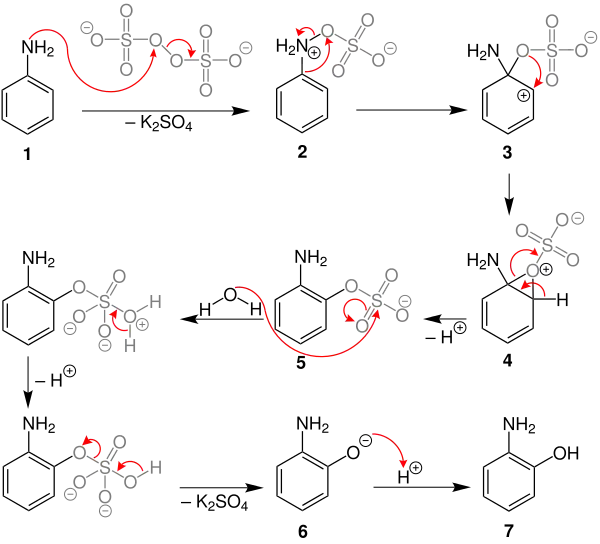
Das freie Elektronenpaar des Stickstoffatoms vom Anilin (1) greift eines der beiden instabilen Sauerstoffatome der Peroxidgruppe vom Kaliumperoxodisulfats an und spaltet dabei Kaliumsulfat ab. Dabei entsteht ein Phenylammoniumsulfat 2. Nun findet der ipso-Angriff der Sulfatgruppe statt, durch die das stabilere Zwischenprodukt 3 gebildet wird und dearomatisiert wird. Durch die Spaltung der Doppelbindung entsteht ein Carbeniumion in ortho-Stellung und dadurch eine Epoxidgruppe 4. Das Wasserstoffatom der Epoxidgruppe 4 spaltet sich ab und rearomatisiert zum ortho-Aminophenylsulfat 5. Durch den Angriff von Wasser an der Sulfatgruppe entsteht über mehrere interne Mechanismen das ortho-Aminophenolat 6. Durch Protonierung des Phenolates wird das Endprodukt ortho-Aminophenol (7) gebildet.
Anwendung
Die Reaktion findet hauptsächlich Anwendung in Vorbereitung und anschließender Weiterverarbeitung von Aminophenolen zu Azofarbstoffen und Schmerzmitteln.[3]
Literatur
- Bradford P. Mundy, Michael G. Ellerd, Frang G. Favaloro Jr.: Name Reactions and Reagents in Organic Synthesis. Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York 2005, ISBN 0-471-22854-0, S. 114.
- Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. John Wiley & Sons, Ney Jersey 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8, S. 497–500.
Einzelnachweise
- E. Boyland, P. Sims, D. C. Williams: The oxidation of tryptophan and some related compounds with persulphate. In: Biochemical Journal. Band 62, Nr. 4, April 1956, S. 546–550, PMID 13315210, PMC 1215958 (freier Volltext).
- Bradford P. Mundy, Michael G. Ellerd, Frang G. Favaloro Jr.: Name Reactions and Reagents in Organic Synthesis. Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York 2005, S. 114.
- Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. John Wiley & Sons, Ney Jersey 2009, S. 498.