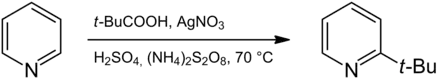2-tert-Butylpyridin
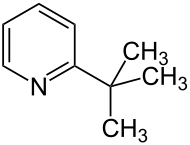
2-tert-Butylpyridin ist eine organische Verbindung, die zu den Heterocyclen (genauer: Heteroaromaten) zählt. Es besteht aus einem Pyridinring, der in 2-Position einen tert-Butylrest trägt.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | 2-tert-Butylpyridin | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
2-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-pyridin | |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C9H13N | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 135,21 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | |||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
schlecht in Wasser (1,8 g·l−1 bei 25 °C)[2] | |||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,4891[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | ||||||||||||||||
Darstellung
Die Verbindung kann aus Pyridin durch radikalische Substitution in einer Minisci-Reaktion hergestellt werden. Hierzu wird Pyridin mit Pivalinsäure, Silbernitrat und Ammoniumperoxodisulfat in schwefelsaurer Lösung zur Reaktion gebracht. Aus Pivalinsäure wird hierbei ein tert-Butylradikal generiert, welches dann mit dem Pyridinring in hoher Selektivität in 2-Position reagiert. Das Produkt wird mit einer exzellenten Ausbeute von 97 % erhalten.[4]
Einzelnachweise
- H. C. Brown, W. A. Murphey: A Convenient Synthesis of the Monoalkylpyridines; a New Prototropic Reaction of 3-Picoline, in: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1951, 73, S. 3308–3312; doi:10.1021/ja01151a093.
- H. P. Hopkins Jr., D. V. Jahagirdar, P. S. Moulik, D. H. Aue, H. M. Webb, W. R. Davidson, M. D. Pedley: Basicities of the 2-, 4-, 2,4-Di-, and 2,6-Disubstituted tert-Butyl Pyridines in the Gas Phase and Aqueous Phase: Steric Effects in the Solvation of tert-Butyl-Substituted Pyridines and Pyridinium Cations, in: J. Am. Chem. Soc, 1984, 106, S. 4341–4348; doi:10.1021/ja00328a007.
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- J. A. Joules, K. Mills: Heterocyclic Chemistry, 5. Auflage, Blackwell Publishing, Chichester, 2010, ISBN 978-1-4051-9365-8, S. 125–141.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.