1,2-Diiodethan
1,2-Diiodethan ist ein zweifach iodiertes Derivat des Ethans und somit ein halogenierter Kohlenwasserstoff. Es ist isomer zu 1,1-Diiodethan.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
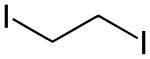 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | 1,2-Diiodethan | |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C2H4I2 | |||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
gelbe monokline Prismen[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 281,86 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | |||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
3,325 g·cm−3 (20 °C)[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
200 °C[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
löslich in Ethanol, Diethylether, Aceton und Chloroform[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,871 (20 °C)[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamische Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔHf0 |
9,3 kJ/mol[3] | |||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | ||||||||||||||||
Eigenschaften
1,2-Diiodethan bildet gelbe monokline Prismen mit einem Schmelzpunkt von 83 °C und einer hohen Dichte von 3,325 g·cm−3. Der kritische Punkt liegt bei einer Temperatur von 749,91 K, einem Druck von 47,30 bar und einem Volumen von 323,5 ml·mol−1.[4]
Verwendung
In der organischen Synthese wird es vor allem zur Darstellung von Samarium(II)-iodid und Ytterbium(II)-iodid in THF verwendet.[5]
Einzelnachweise
- David R. Lide (Hrsg.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 90. Auflage. (Internet-Version: 2010), CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, S. 3-184.
- Datenblatt 1,2-Diiodethan bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 15. März 2011 (PDF).
- David R. Lide (Hrsg.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 90. Auflage. (Internet-Version: 2010), CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, S. 5-22.
- Carl L. Yaws: "Thermophysical properties of chemicals and hydrocarbons", S. 6 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- P. Girard, Jean-Louis Namy, Henri B. Kagan: "Divalent Lanthanide Derivatives in Organic Synthesis. 1. Mild Preparation of SmI2 and YbI2 and Their Use as Reducing or Coupling Agents", in: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1980, 102 (8), S. 2693–2698 (doi:10.1021/ja00528a029).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.
