Bokak
Bokak oder auch Taongi (deutsch veraltet: Petrelinsel[1]; Gaspar Rico und Smyth Island) ist das nördlichste Atoll der Ratak-Kette und somit die nördlichste Landmasse der Marshallinseln. Das unbewohnte Atoll hat eine Landfläche von 1,25 km² bei einer Lagunenfläche von 30,31 km². Das 280 km entfernte Atoll Bikar liegt Bokak am nächsten.
| Bokak (Taongi) | ||
|---|---|---|
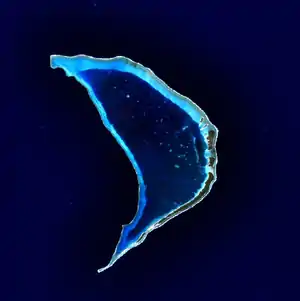 NASA-Bild von Bokak | ||
| Gewässer | Pazifischer Ozean | |
| Archipel | Marshallinseln | |
| Geographische Lage | 14° 31′ N, 169° 0′ O | |
| ||
| Anzahl der Inseln | 10 | |
| Hauptinsel | Sibylla Island (Bok-Ak) | |
| Landfläche | 2,0 km² | |
| Lagunenfläche | 48,5 km² | |
| Einwohner | unbewohnt (2002) | |
.jpg.webp) Karte des Atolls | ||
Die wichtigsten Inseln, von Norden nach Süden aus gesehen, sind:[2]
- North Island
- Kamwome
- Bwdije (Bwideje)
- Sibylla Island (Jipila)
- Pokak (Bok-ak)
- Bwokwla (Bok-ḷā)
Das Atoll wurde von Alonso de Salazar am 21. August 1526 entdeckt.
Auf der Insel sind u. a. Fregattvögel und die Australische Seeschwalbe heimisch.
Literatur
- James E. Maragos: Description of reefs and corals for the 1988 protected area survey of the Northern Marshall Islands, Atoll Research Bulletin, No. 419, August 1994 (PDF; 11,6 MB)
- David Stanley:Mikronesien Handbuch;Verlag Gisela E. Walther;1987;S.76
Weblinks
- Bild und Kurzbeschreibung (engl.) (Memento vom 23. Dezember 2010 im Internet Archive)
- Bilder und Kurzbeschreibung der Vogelwelt (englisch)
- Geographische Informationen (englisch)
Einzelnachweise
- Deutsches Koloniallexikon. Hrsg. von Heinrich Schnee. - Leipzig: Quelle & Meyer 1920. - 3 Bde.
- Place Names of the Marshall Islands (from the PALI edition of the Marshallese-English Dictionary) (Namensvarianten)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.