4-Vinylcyclohexendioxid
4-Vinylcyclohexendioxid ist ein cycloaliphatisches Epoxid, das als Monomer zur Herstellung vernetzter Epoxidharze[6] und als Zwischenprodukt zur Synthese organischer Verbindungen industriell verwendet wird.[3]
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
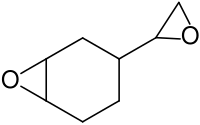 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Komplexes Stereoisomerengemisch – Strukturformel ohne Stereochemie | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | 4-Vinylcyclohexendioxid | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C8H12O2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
farblose Flüssigkeit[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 140,182 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte | |||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt |
−108,9 °C[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
227 °C[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dampfdruck | |||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
leicht in Wasser[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,4738[3] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Toxikologische Daten | |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | |||||||||||||||||||
Herstellung
4-Vinylcyclohexendioxid wird durch Epoxidierung von 4-Vinylcyclohexen mit Persäure hergestellt.[7]
Eigenschaften
4-Vinylcyclohexendioxid besitzt eine Viskosität von 15 mPa·s.[7]
Einzelnachweise
- Kam-Piu Ho, Wing-Leung Wong, Kin-Ming Lam, Cheuk-Piu Lai, Tak Hang Chan und Kwok-Yin Wong: A Simple and Effective Catalytic System for Epoxidation of Aliphatic Terminal Alkenes with Manganese(II) as the Catalyst. In: Chemistry - A European Journal. 14, Nr. 26, 8. September 2008, S. 7988–7996. doi:10.1002/chem.200800759.
- Eintrag zu 1-Epoxyethyl-3,4-epoxycyclohexan in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 20. Januar 2022. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- Kh. M. Alimardanov, O. A. Sadygov, N. I. Garibov und M. Ya. Abdullaeva: Liquid-phase synthesis of cyclic diene diepoxides using metal halides and hydrogen peroxide. In: Russian Journal of Organic Chemistry. 48, Nr. 10, 7. November 2012, S. 1302–1308. doi:10.1134/S1070428012100077.
- L. A. Mukhamedova, G. Kh. Gil'manova, M. I. Kudryavtseva, F. G. Nasybullina und A. S. Kireeva: Synthesis and testing of the antiviral activity of epoxy and triazo derivatives of cyclohexane. In: Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 16, Nr. 7, Juli 1982, S. 510–514. doi:10.1007/BF00761540.
- Eintrag zu 7-oxa-3-oxiranylbicyclo[4.1.0]heptane im Classification and Labelling Inventory der Europäischen Chemikalienagentur (ECHA), abgerufen am 1. August 2016. Hersteller bzw. Inverkehrbringer können die harmonisierte Einstufung und Kennzeichnung erweitern.
- Patent US2555500: Copolymers of 4-vinylcyclohexene dioxide. Veröffentlicht am 25. Januar 1949, Erfinder: Hart Segall Gordon.
- Ha Q. Pham, Maurice J. Marks: Epoxy Resins. In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. März. doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_547.pub2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.

