1-Phenyl-1-propanol
1-Phenyl-1-propanol ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Alkohole und ein Derivat des Benzylalkohols.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
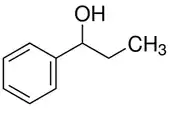 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | 1-Phenyl-1-propanol | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C9H12O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
farblose Flüssigkeit[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 136,19 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
0,994 g·cm−3 (25 °C)[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,52 (20 °C)[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Toxikologische Daten | |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | |||||||||||||||||||
Isomere
1-Phenyl-1-propanol ist chiral und kommt in zwei enantiomeren Formen, (R)-(+)-1-Phenyl-1-propanol und (S)-(−)-1-Phenyl-1-propanol, vor.
| Isomere von 1-Phenyl-1-propanol | ||
| Name | (R)-(+)-1-Phenyl-1-propanol | (S)-(−)-1-Phenyl-1-propanol |
| Strukturformel | -(%252B)-1-Phenyl-1-propanol_Structural_formula_V2.svg.png.webp) |
-(%E2%80%93)-1-Phenyl-1-propanol_Structural_formula_V2.svg.png.webp) |
| CAS-Nummer | 1565-74-8 | 613-87-6 |
| 93-54-9 (unspez.) | ||
| EG-Nummer | 625-112-2 | 624-364-0 |
| 202-256-0 (unspez.) | ||
| ECHA-Infocard | 100.153.639 | 100.152.961 |
| 100.002.052 (unspez.) | ||
| PubChem | – | – |
| 7147 (unspez.) | ||
| Wikidata | Q72472788 | Q72498397 |
| Q15726117 (unspez.) | ||
| Siedetemperatur | 218–220 °C[2] | 94–95 °C (10 mmHg)[3] |
| 103 °C (14 mmHg)[1] (unspez.) | ||
Gewinnung und Darstellung
1-Phenyl-1-propanol kann durch eine Grignard-Reaktion von Brombenzol oder Phenylmagnesiumbromid mit Propionaldehyd gewonnen werden.[4]
Auch eine Biosynthese von (R)-1-Phenyl-1-propanol durch den Schlauchpilz Fusarium moniliforme wurde beschrieben.[5]
Verwendung
1-Phenyl-1-propanol wird als Rohstoff und Zwischenprodukt für organischen Synthesen verwendet.
Einzelnachweise
- Datenblatt 1-Phenyl-1-propanol, 97% bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 5. September 2021 (PDF).
- Datenblatt (R)-(+)-1-Phenyl-1-propanol, 99% bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 22. September 2021 (PDF).
- Datenblatt (S)-(+)-1-Phenyl-1-propanol, 99% bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 22. September 2021 (PDF).
- C. Blomberg, J. Coops: Asymmetric syntheses by Grignard compounds prepared in optically active solvents: Part I. Optically active monofunctional ethers. In: Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas. Band 83, Nr. 10, 1964, S. 1083–1095, doi:10.1002/recl.19640831012.
- Atsuko Uzura, Tohoru Katsuragi, Yoshiki Tani: Optimal Conditions for Production of (R)-1-Phenylpropanol by Fusarium moniliforme Strain MS31. In: Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 92, 2001, S. 288, doi:10.1263/jbb.92.288, PMID 16233098.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.
