U0126
U0126 ist ein selektiver Inhibitor der Enzyme MEK 1 und 2 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase family members) im MAP-Kinase-Weg.[3][4]
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
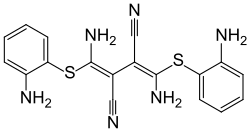 | |||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||
| Name | U0126 | ||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C18H16N6S2 | ||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung | |||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 380,49 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | ||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt |
172–173 °C (Monoethanolat)[2] | ||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit | |||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||
Eigenschaften
Bei einer Hemmung mit U0126 wird der Transkriptionsfaktor AP-1 nichtkompetitiv mit einer IC50 von 72 nM bei MEK1 und 58 nM bei MEK2. Dabei wird auch der mTOR-p70(S6K)-Weg gehemmt. U0126 zeigt anti-Tumor-Wirkungen und verstärkt eine Anoikis in Zellkulturen.[5] U0126 ist auch ein Hemmer von PKC, Raf, JNK, MEKK, MKK-3, MKK-4/SEK, MKK-6, Cdk2 und Cdk4. U0126 aktiviert den Aryl-Hydrocarbon-Rezeptor und die Genexpression von CYP1A und CYP3A.[6][7]
Anwendungen
Eine Verwendung von U0126 zur Behandlung von posttraumatischen Belastungsstörungen wird untersucht.[8] U0126 schützt Nervenzellen vor oxidativem Stress in Zellkulturen.[9] U0126 verlangsamt die Wallersche Degeneration nach einer Verletzung von Nervenzellen.[10]
Einzelnachweise
- Datenblatt U0126, 99+% bei AlfaAesar, abgerufen am 13. Januar 2015 (PDF) (JavaScript erforderlich).
- Datenblatt U0126 monoethanolate, ≥98% (HPLC), powder bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 13. Januar 2015 (PDF).
- M. F. Favata, K. Y. Horiuchi, E. J. Manos, A. J. Daulerio, D. A. Stradley, W. S. Feeser, D. E. Van Dyk, W. J. Pitts, R. A. Earl, F. Hobbs, R. A. Copeland, R. L. Magolda, P. A. Scherle, J. M. Trzaskos: Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. In: The Journal of Biological Chemistry. Band 273, Nummer 29, Juli 1998, S. 18623–18632, PMID 9660836.
- J. V. Duncia, J. B. Santella, C. A. Higley, W. J. Pitts, J. Wityak, W. E. Frietze, F. W. Rankin, J. H. Sun, R. A. Earl, A. C. Tabaka, C. A. Teleha, K. F. Blom, M. F. Favata, E. J. Manos, A. J. Daulerio, D. A. Stradley, K. Horiuchi, R. A. Copeland, P. A. Scherle, J. M. Trzaskos, R. L. Magolda, G. L. Trainor, R. R. Wexler, F. W. Hobbs, R. E. Olson: MEK inhibitors: the chemistry and biological activity of U0126, its analogs, and cyclization products. In: Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. Band 8, Nummer 20, Oktober 1998, S. 2839–2844, PMID 9873633.
- H. Fukazawa, K. Noguchi, Y. Murakami, Y. Uehara: Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors restore anoikis sensitivity in human breast cancer cell lines with a constitutively activated extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. In: Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. Band 1, Nummer 5, März 2002, S. 303–309, PMID 12489846.
- P. Bachleda, Z. Dvorák: Pharmacological inhibitors of JNK and ERK kinases SP600125 and U0126 are not appropriate tools for studies of drug metabolism because they activate aryl hydrocarbon receptor. In: General Physiology and Biophysics. Band 27, Nummer 2, Juni 2008, S. 143–145, PMID 18645229.
- T. Smutny, M. Bitman, M. Urban, M. Dubecka, R. Vrzal, Z. Dvorak, P. Pavek: U0126, a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 and 2 (MEK1 and 2) inhibitor, selectively up-regulates main isoforms of CYP3A subfamily via a pregnane X receptor (PXR) in HepG2 cells. In: Archives of Toxicology. Band 88, Nummer 12, Dezember 2014, S. 2243–2259, doi:10.1007/s00204-014-1254-2. PMID 24819614.
- V. Doyère, J. Debiec, M. H. Monfils, G. E. Schafe, J. E. LeDoux: Synapse-specific reconsolidation of distinct fear memories in the lateral amygdala. In: Nature Neuroscience. Band 10, Nummer 4, April 2007, S. 414–416, doi:10.1038/nn1871. PMID 17351634.
- Q. Ong, S. Guo, K. Zhang, B. Cui: U0126 Protects Cells against Oxidative Stress Independent of Its Function as a MEK Inhibitor. In: ACS Chemical Neuroscience. [elektronische Veröffentlichung vor dem Druck] Januar 2015, doi:10.1021/cn500288n. PMID 25544156.
- C. Evans, S. J. Cook, M. P. Coleman, J. Gilley: MEK inhibitor U0126 reverses protection of axons from Wallerian degeneration independently of MEK-ERK signaling. In: PLOS ONE. Band 8, Nummer 10, 2013, S. e76505, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076505. PMID 24124570. PMC 3790678 (freier Volltext).
