Tymovirales
Die Ordnung Tymovirales ist ein Taxon (Verwandtschaftsgruppe) von Viren mit einzelsträngigem RNA-Genom in positiv-Strang-Orientierung, das linear und nicht segmentiert ist. Ihre Vertreter sind überwiegend Pflanzenviren. Der Name für Ordnung ist von der Virusfamilie Tymoviridae und diese wiederum von ihrer Typspezies, dem Turnip yellow mosaic virus abgeleitet.
| Tymovirales | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Narzissen-Mosaikvirus (NMV), | ||||||||||||
| Systematik | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Taxonomische Merkmale | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Wissenschaftlicher Name | ||||||||||||
| Tymovirales | ||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||
|
Beschreibung
Während die Virusteilchen (Virionen) der Vertreter der Familie Tymoviridae aus isometrischen, ikosaedrischen Kapsiden bestehen, findet man bei den anderen drei Familien filamentöse, helikale Kapsidsymmetrien. Aufgrund von Sequenzähnlichkeiten und ähnlichen Replikationsstrategien ist jedoch ein gemeinsamer evolutionärer Vorläufer für alle vier Familien anzunehmen, weshalb 2011 vom ICTV die neue Ordnung Tymovirales geschaffen wurde.
Systematik
Innere Systematik
Nach der offiziellen Virus-Taxonomie des ICTV, Stand November 2018, umfasst die Ordnung Tymovirales folgende Familien:
- Familie Alphaflexiviridae[3]
- Gattung Allexivirus[4]
- Gattung Botrexvirus
- Gattung Lolavirus
- Gattung Mandarivirus[6]
- Gattung Platypuvirus
- Gattung Potexvirus[7]
- Gattung Sclerodarnavirus
- Familie Betaflexiviridae[8]
- Unterfamilie Quinvirinae
- Gattung Carlavirus[9]
- Gattung Foveavirus[10]
- Spezies Apple stem pitting virus (ASPV, Typus)
- Gattung Robigovirus
- Unterfamilie Trivirinae
- Gattung Capillovirus[11]
- Spezies Apple stem grooving virus (ASGV, Typus)
- Gattung Chordovirus
- Gattung Citrivirus
- Spezies Citrus leaf blotch virus (CLBV, Typus)
- Gattung Divavirus
- Gattung Prunevirus
- Gattung Tepovirus
- Gattung Trichovirus[12]
- Spezies Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus (ACLSV, Typus)
- Spezies Cherry mottle leaf virus (CMLV)
- Gattung Vitivirus[13]
- Spezies Grapevine virus A (GVA, Typus)
- Spezies Grapevine virus B (GVB)
- Familie Gammaflexiviridae[14]
- Gattung Mycoflexivirus
- Spezies Botrytis virus F (Typus)
- Familie Deltaflexiviridae[15]
- Gattung Deltaflexivirus
- Spezies Sclerotinia deltaflexivirus 1 (Typus)
- Familie Tymoviridae[16]
- Gattung Maculavirus
- Gattung Marafivirus
- Gattung Tymovirus
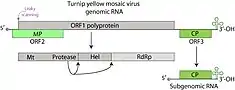
- Spezies Gelbe-Rüben-Mosaikvirus, alias Rübenmosaikvirus, en. Turnip yellow mosaic virus (TYMV, Typus)
- Spezies Mildes Anden-Kartoffelmosaikvirus, en. Andean potato mild mosaic virus (APMMV0)
Äußere Systematik
Koonin et al haben 2015 die Tymovirales taxonomisch (aufgrund ihrer Verwandtschaft) der von ihnen postulierten Supergruppe ‚Alphavirus-like superfamily‘ zugeordnet.[17] Der Stammbaum dieser Supergruppe ist nach den Autoren wie folgt:[18]
| „Alphavirus-like superfamily“ |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Die Mitglieder dieser vorgeschlagenen Supergruppe gehören verschiedenen Gruppen der Baltimore-Klassifikation an, in der Regel handelt es sich um einzelsträngige RNA-Viren positiver Polarität ((+)ssRNA, Baltimore-Gruppe 4), es sind aber auch – wie die Birnaviridae – doppelsträngige Vertreter (mit dsRNA gekennzeichnet, Baltimore-Gruppe 3) zu finden.
ICTV Master Species List #35
Mit der neuen Master species List des ICTV, ratifiziert im März 2020, ergibt sich abweichend folgendes Bild:[2]
| Orthornavirae |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Von den Kitrinoviricota sind nur die Klassen mit den bereits genannten Familien gelistet, zwei weitere dieser Familien bleiben mit diesem Stand innerhalb der Orthornavirae noch ohne Zuordnung. Die „Alphavirus-like superfamily“ deckt sich im Wesentlichen mit dem Phylum Kitrinoviricota.
Als mögliches weiteres Mitglied dieses Phylums könnte eine vorgeschlagene Familie um das Chronische Bienenlähmungsvirus (CBPV) infrage kommen, wenn die Nodaviridae und die Tombusviridae dessen nächste Verwandte sind, die Unterschiede aber eine eigene Familie rechtfertigen (siehe dort).
Quellen
- A. M. Q. King, M. J. Adams, E. B. Carstens, E. J. Lefkowitz (eds.): Virus Taxonomy. Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Amsterdam 2012, ISBN 978-0-12-384684-6, S. 901ff
Einzelnachweise
- ICTV Master Species List 2018b v1 MSL #34, Feb. 2019
- ICTV: ICTV Master Species List 2019.v1, New MSL including all taxa updates since the 2018b release, March 2020 (MSL #35)
- SIB: Alphaflexiviridae, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Allexivirus, auf: ViralZone
- S. Majumder, M. Arya, R. P. Pant, V. K. Baranwal: Shallot virus X in Indian shallot, a new virus report for India, in: New Disease Reports (2007) 15, 52, ISSN 2044-0588
- SIB: Mandarivirus, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Potexvirus, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Betaflexiviridae, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Carlavirus, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Foveavirus, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Capillovirus, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Trichovirus, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Vitivirus, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Gammaflexiviridae, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Deltaflexiviridae, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Tymoviridae, auf: ViralZone
- In älteren Arbeiten findet sich (mit abweichender Phylogenie) auch die Bezeichnung ‚Sindbis-like supergroup‘, Sindbis-Virus ist eine Spezies in der Gattung Alphavirus, Familie Togaviridae. Da diese Gruppe (von den Autoren als englisch superfamily bezeichnet) mit den Tymovirales eine Ordnung enthält, muss ihr Rang höher sein als dieser und ist nicht etwa als Überfamilie zu verstehen. Ränge höher als Ordnung waren zum Zeitpunkt der Arbeit vom ICTV aber noch gar nicht vorgegeben.
- Eugene V. Koonin, Valerian V. Dolja, Mart Krupovic: Origins and evolution of viruses of eukaryotes: The ultimate modularity, in: Virology vom Mai 2015; 479-480. 2–25, Epub 12. März 2015, PMC 5898234 (freier Volltext), PMID 25771806
- SIB: Alphatetraviridae, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Carmotetraviridae, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Permutotetraviridae, auf: ViralZone
- SIB: Nodaviridae, auf: ViralZone
- ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: Alfalfa enamovirus 1, EC 51, Berlin, Germany, July 2019; Email ratification March 2020 (MSL #35)