Methylfluorsulfonat
Methylfluorsulfonat (umgangssprachlich auch magic methyl) ist ein Methylierungsreagenz.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
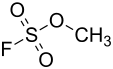 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | Methylfluorsulfonat | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | CH3FO3S | |||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
farblose Flüssigkeit[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 114,09 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
1,45 g·cm−3[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt |
−95 °C[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
93 °C[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,3325 (20 °C)[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | ||||||||||||||||
Eigenschaften
Methylfluorsulfonat wird durch Destillation einer äquimolaren Mischung aus Fluorsulfonsäure und Dimethylsulfat erzeugt. Es ist um etwa vier Größenordnungen reaktiver als Methyliodid. In biologischen Geweben wirkt die Methylierung von Biomolekülen durch Methylfluorsulfonat akut toxisch (LC50 (Ratte) ~ 5 ppm),[3] mutagen[4] und erzeugt eine Reizung der Atemwege und ein Lungenödem.
| Eigenschaft | Wert |
|---|---|
| Wasserstoffbrückenakzeptor | 3 |
| Wasserstoffbrückendonor | 0 |
| Octanol-Wasser-Verteilungskoeffizient[5][6] | –0,3 ALogP |
| Löslichkeit[7] (log Solubility) | –0,9 log mol/L |
| Polar Surface Area[8] (PSA) | 51,8 Å2 |
Siehe auch
- Methyltrifluormethylsulfonat, ein ähnlich starkes, etwas häufiger angewendetes Methylierungsmittel[9]
Einzelnachweise
- Lide: 1998 Freshman Achievement Award. CRC Press, 1998, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2, S. 3–352 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- TCI: Methyl Fluorosulfonate (stabilized with KF), abgerufen am 8. April 2014
- Hite, M., Rinehart, W.; Braun, W.; Peck, H.: Acute toxicity of methyl fluorosulfonate (Magic Methyl). In: AIHA Journal. 40, Nr. 7, 1979, S. 600–603. doi:10.1080/00028897708984416. PMID 484483.
- J. Ashby, D. Anderson, J. A. Styles: The potential carcinogenicity of methyl fluorosulphonate (CH3OSO2F; Magic Methyl). In: Mutation Research. Band 51, Nummer 2, August 1978, S. 285–287, PMID 211408.
- Arup K. Ghose, Vellarkad N. Viswanadhan, John J. Wendoloski: Prediction of Hydrophobic (Lipophilic) Properties of Small Organic Molecules Using Fragmental Methods: An Analysis of ALOGP and CLOGP Methods. In: The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 102, 1998, S. 3762–3772, doi:10.1021/jp980230o.
- Arup K. Ghose, Vellarkad N. Viswanadhan, John J. Wendoloski: Prediction of Hydrophobic (Lipophilic) Properties of Small Organic Molecules Using Fragmental Methods: An Analysis of ALOGP and CLOGP Methods. In: The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 102, 1998, S. 3762, doi:10.1021/jp980230o.
- I. V. Tetko, V. Y. Tanchuk, T. N. Kasheva, A. E. Villa: Estimation of aqueous solubility of chemical compounds using E-state indices. In: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences. Band 41, Nummer 6, 2001 Nov-Dec, S. 1488–1493, PMID 11749573.
- P. Ertl, B. Rohde, P. Selzer: Fast calculation of molecular polar surface area as a sum of fragment-based contributions and its application to the prediction of drug transport properties. In: Journal of medicinal chemistry. Band 43, Nummer 20, Oktober 2000, S. 3714–3717, ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 11020286.
- Roger W. Alder, Justin G. E. Phillips, Lijun Huang, Xuefei Huang: Methyltrifluoromethanesulfonate Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 2005, John Wiley & Sons, doi:10.1002/047084289X.rm266m.pub2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.