Iodbenzoldichlorid
Iodbenzoldichlorid (PhICl2) ist eine chemische Verbindung aus Iodbenzol und Chlor, die hauptsächlich als Oxidations- und Chlorierungsmittel verwendet wird.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
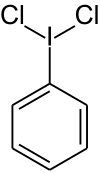 | |||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||
| Name | Iodbenzoldichlorid | ||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C6H5Cl2I | ||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
gelber Feststoff[1] | ||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 274,1 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||
| Dichte |
2,2 g·cm−3[1] | ||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt |
115–120 °C[1] | ||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||
Struktur
Laut Kristallstrukturanalyse handelt es sich um eine T-förmige Struktur mit einem zentralen Iod-Atom. Entsprechende Vorhersagen mit dem VSEPR-Modell wurden damit bestätigt.[3][4]
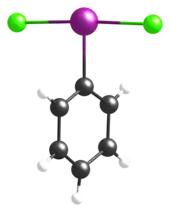
Darstellung
Iodbenzoldichlorid ist eine instabile Verbindung. Gewonnen werden kann sie durch eine Fällungsreaktion, indem Chlorgas durch eine Lösung von Iodbenzol in Chloroform geleitet wird, wobei Iodbenzoldichlorid ausfällt.[5] Dieser Syntheseweg wird sowohl im Labor, als auch bei der Herstellung im industriellen Maßstab angewendet.[6]
Alternativ besteht auch die Möglichkeit, das benötigte Chlor in situ aus Natriumhypochlorit und Salzsäure herzustellen.[7]
Reaktionen
Durch Hydrolyse in basischer Lösung entsteht Iodosobenzol[5] (PhIO) und durch Oxidation, beispielsweise mit Natriumhypochlorit, entsteht Iodoxybenzol.[8]
In der organischen Synthese kann Iodbenzoldichlorid verwendet werden, um Alkene[1] und Alkine[9] selektiv zu chlorieren.
Einzelnachweise
- David W. Knight, Glen A. Russell: Phenyliodine(III) Dichloride. In: Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. American Cancer Society, 2001, ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8, doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp071.
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- E. M. Archer, T. G. van Schalkwyk: The crystal structure of benzene iododichloride. In: Acta Crystallographica. Band 6, Nr. 1, 10. Januar 1953, S. 88–92, doi:10.1107/S0365110X53000193 (iucr.org).
- J. V. Carey, P. A. Chaloner, P. B. Hitchcock, T. Neugebauer, K. R. Seddon: Synthesis and Decomposition of Dichloroiodoarenes. An Improved Low Temperature X-Ray Structure of Dichloroiodobenzene and the Structure of 1-Chloro-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(chloromethyl)-4-methylbenzene. In: ChemInform. Band 27, Nr. 52, 1996, doi:10.1002/chin.199652032.
- H. J. Lucas and E. R. Kennedy: Iodobenzene dichloride In: Organic Syntheses. 22, 1942, S. 69, doi:10.15227/orgsyn.022.0069; Coll. Vol. 3, 1955, S. 482 (PDF).
- Atsuhiko Zanka, Hiroki Takeuchi, Ariyoshi Kubota: Large-Scale Preparation of Iodobenzene Dichloride and Efficient Monochlorination of 4-Aminoacetophenone. In: Organic Process Research & Development. Band 2, Nr. 4, 1. Juli 1998, S. 270–273, doi:10.1021/op980024e.
- Xue-Fei Zhao, Chi Zhang: Iodobenzene Dichloride as a Stoichiometric Oxidant for the Conversion of Alcohols into Carbonyl Compounds; Two Facile Methods for Its Preparation. In: Synthesis. Band 2007, Nr. 04, Februar 2007, S. 551–557, doi:10.1055/s-2007-965889.
- M. W. Formo and John R. Johnson: Iodoxybenzene: B. Hypochlorite oxidation of iodobenzene dichloride In: Organic Syntheses. 22, 1942, S. 72, doi:10.15227/orgsyn.022.0072; Coll. Vol. 3, 1955, S. 485 (PDF).
- Michael E. Jung, Michael H. Parker: Synthesis of Several Naturally Occurring Polyhalogenated Monoterpenes of the Halomon Class1. In: The Journal of Organic Chemistry. Band 62, Nr. 21, 1. Oktober 1997, S. 7094–7095, doi:10.1021/jo971371+, PMID 11671809.