Decafluorbutan
Decafluorbutan ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Fluorkohlenwasserstoffe.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
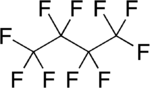 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Decafluorbutan | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
Perfluorbutan | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C4F10 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
farbloses Gas[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 238,03 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
gasförmig | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
−1,9 °C[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
löslich in Benzol und Chloroform[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treibhauspotential |
10213 (bezogen auf 100 Jahre)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Gewinnung und Darstellung
Decafluorbutan kann durch Reaktion von Graphit mit Fluor oder elektrochemische Fluorierung von Tributylamin mit Fluorwasserstoff gewonnen werden.[4][5] Es sind noch weitere Syntheseverfahren, zum Beispiel aus Polyfluorpolyhalogenbutenen, bekannt.[6][7]
Eigenschaften
Decafluorbutan ist ein farbloses Gas, das löslich in Benzol und Chloroform ist.[1]
Verwendung
Decafluorbutan kann in der medizinischen Forschung verwendet werden.[8]
Einzelnachweise
- David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics A Ready-reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-0595-5, S. 456 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- G. Myhre, D. Shindell et al.: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. Hrsg.: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2013, Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing, S. 24–39; Table 8.SM.16 (ipcc.ch [PDF]).
- G. G. Shelopin, D. S. Pashkevich u. a.: Synthesis of perfluoroalkanes by fluorination of graphite with elementary fluorine in a vertical ascending gas-dust flow. In: Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry. 79, 2006, S. 941, doi:10.1134/S1070427206060140.
- December 2006 — "Implementing methods for contact of fluorine and graphite during synthesis of lowest perfluoroalkanes": Volume # 6(49), November - December 2006 — "Implementing methods for contact of fluorine and graphite during synthesis of lowest perfluoroalkanes", abgerufen am 6. April 2019
- Houben-Weyl Methods of Organic Chemistry Vol. V/3, 4th Edition Fluorine and Chlorine Compounds. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 3-13-179994-3, S. 336 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Günther Schiemann: Die Organischen Fluorverbindungen in ihrer Bedeutung für die Technik. Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-95940-0, S. 145 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Paul S. Sheeran, Vincent P. Wong u. a.: Decafluorobutane as a Phase-Change Contrast Agent for Low-Energy Extravascular Ultrasonic Imaging. In: Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology. 37, 2011, S. 1518, doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2011.05.021.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.