Bipyridine
Unter Bipyridinen fasst man eine Gruppe organischer Verbindungen zusammen. Als gemeinsames strukturgebendes Element besitzen sie zwei Pyridinringe, die direkt miteinander verknüpft sind. Da es an jedem Pyridinmolekül drei verschiedene Verknüpfungspositionen gibt, existieren zur Bildung des Grundgerüsts sechs mögliche Isomere. Die Isomere 2,2′-, 3,3′- und 4,4′-Bipyridin sind formal symmetrisch aufgebaut, 2,3′-, 2,4′- und 3,4′-Bipyridin asymmetrisch.[1] 2,2′- und das 4,4′-Bipyridin haben Bedeutung als Liganden in der Komplexchemie erlangt.[1][2]
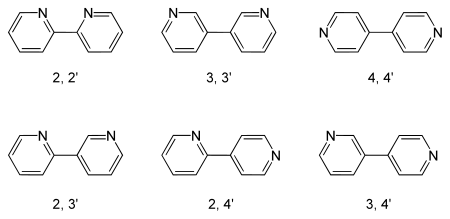
Überblick über mögliche Bipyridin-Strukturen
Weblinks
Commons: Bipyridine – Sammlung von Bildern, Videos und Audiodateien
Einzelnachweise
- Christian Kaes, Alexander Katz, Mir Wais Hosseini: Bipyridine: The Most Widely Used Ligand. A Review of Molecules Comprising at Least Two 2,2′-Bipyridine Units. In: Chemical Reviews. Band 100, Nr. 10, 2000, S. 3553–3590, doi:10.1021/cr990376z.
- Boris I. Kharisov, Perla Elizondo Martínez, Víctor M. Jiménez-Pérez, Oxana V. Kharissova, Blanca Nájera Martínez, Nancy Pérez: Recent advances on ditopic ligands. In: Journal of Coordination Chemistry. Band 63, Nr. 1, 2010, S. 1–25, doi:10.1080/00958970903325534.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.