Tryptophol
Tryptophol ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Indolderivate und Alkohole.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
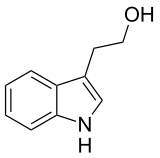 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Tryptophol | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C10H11NO | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 161,20 g·mol[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
Fest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||||||||
Vorkommen
Tryptophol kommt natürlich in den Nadeln und Samen der Waldkiefer vor.[2] Daneben entsteht Tryptophol bei der alkoholischen Fermentation[3] als Sekundärprodukt und ist im Wein[4] und Bier enthalten. Tryptophol wird auch von der Pilzart Candida albicans[5] oder von der Schwammart Ircinia spiculosa erzeugt.[6]
Vorläufer für die Synthese anderer Verbindungen
Tryptophol wurde als Ausgangsstoff bei der Synthese von Dimethyltryptamin[7] und Indoramin verwendet.
Einzelnachweise
- Datenblatt 3-(2-Hydroxyethyl)indole, 98.0% bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 14. April 2017 (PDF).
- Göran Sandberg: Biosynthesis and metabolism of indole-3-ethanol and indole-3-acetic acid by Pinus sylvestris L. Needles. In: Planta. 161, Nr. 5, 1984, S. 398–403. doi:10.1007/BF00394569.
- P Ribéreau-Gayon, JC Sapis: On the presence in wine of tyrosol, tryptophol, phenylethyl alcohol and gamma-butyrolactone, secondary products of alcoholic fermentation. In: Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des seances de l'Academie des sciences. Serie D: Sciences naturelles. 261, Nr. 8, 1965, S. 1915–6. PMID 4954284. (Article in French)
- C. Gil, C. Gómez-Cordovés: Tryptophol content of young wines made from Tempranillo, Garnacha, Viura and Airén grapes. In: Food Chemistry. 22, 1986, S. 59–65. doi:10.1016/0308-8146(86)90009-9.
- BT Lingappa, M Prasad, Y Lingappa, DF Hunt, K Biemann: Phenethyl alcohol and tryptophol: Autoantibiotics produced by the fungus Candida albicans. In: Science. 163, Nr. 3863, 1969, S. 192–4. doi:10.1126/science.163.3863.192. PMID 5762768.
- I ErdoĞAn i, B Sener, T Higa: Tryptophol, a plant auxin isolated from the marine sponge Ircinia spinulosa. In: Biochemical systematics and ecology. 28, Nr. 8, 2000, S. 793–794. doi:10.1016/S0305-1978(99)00111-8. PMID 10856636.
- Dialkyltryptamines via Tryptophol. Erowid.org. Abgerufen am 18. August 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.