Thyreoperoxidase
Thyreoperoxidase (TPO) (auch: Iodid-Peroxidase,[1] systematischer Name: Iodid-Wasserstoffperoxid-Oxidoreduktase) heißt das Enzym, das den ersten Reaktionsschritt in der Synthese der Schilddrüsenhormone aus der Aminosäure Tyrosin katalysiert. Das Enzym wird in allen Chordatieren produziert. Defekte im Enzym aufgrund von Mutationen im TPO-Gen können beim Menschen zu speziellen Formen der Hypothyreose führen.[2]
| Thyreoperoxidase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 919 Aminosäuren | |
| Sekundär- bis Quartärstruktur | Heterodimer | |
| Kofaktor | Ca2+, Häm b | |
| Isoformen | TPO1, TPO2, TPO3, TPO4, TPO5, TPO6, 2-3, 2-4 | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Gen-Name | TPO | |
| Externe IDs | ||
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 1.11.1.8, Oxidoreduktase | |
| Reaktionsart | Redoxreaktion | |
| Substrat | Iodid, H2O2 | |
| Produkte | Iod, H2O | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Homologie-Familie | Hämperoxidasen | |
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Chordatiere | |
Die Thyreoperoxidase ist ein Transmembranprotein, welches in der apikalen Zellmembran von Schilddrüsenzellen vorkommt. Bei verschiedenen Autoimmunerkrankungen der Schilddrüse (Autoimmunthyreopathien) können Autoantikörper gegen die Thyreoperoxidase (Thyreoperoxidase-Antikörper, TPO-AK) nachgewiesen werden.[3][4][5]
Katalysierte Reaktionen
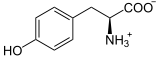 + I− + H+ + H2O2 ⇒
+ I− + H+ + H2O2 ⇒ 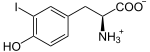 + 2 H2O
+ 2 H2O
Iodid wird zu Iod oxidiert, welches sofort an Tyrosin substituiert.
 + I− + H+ + H2O2 ⇒
+ I− + H+ + H2O2 ⇒ 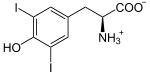 + 2 H2O
+ 2 H2O
Iodid wird zu Iod oxidiert, welches sofort an 3-Iodtyrosin substituiert.
Weiterführende Literatur
- Lothar-Andreas Hotze, Petra-Maria Schumm-Draeger. Schilddrüsenkrankheiten. Diagnose und Therapie. Berlin 2003, ISBN 3-88040-002-4.
- T. Hosoya, Y. Kondo, N. Ui: Peroxidase activity in thyroid gland and partial purification of the enzyme. In: Journal of Biochemistry. Band 52, September 1962, ISSN 0021-924X, S. 180–189, PMID 13964156.
- Noeleen B. Loughran, Brendan O’Connor, Ciarán Ó’Fágáin, Mary J. O’Connell: The phylogeny of the mammalian heme peroxidases and the evolution of their diverse functions. In: BMC Evolutionary Biology. Band 8, 2008, ISSN 1471-2148, S. 101, doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-101, PMID 18371223, PMC 2315650 (freier Volltext).
- Y. Song, N. Driessens, M. Costa, X. De Deken, V. Detours, B. Corvilain, C. Maenhaut, F. Miot, J. Van Sande, M.-C. Many, J. E. Dumont: Roles of hydrogen peroxide in thyroid physiology and disease. In: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. Band 92, Nr. 10, Oktober 2007, ISSN 0021-972X, S. 3764–3773, doi:10.1210/jc.2007-0660, PMID 17666482.
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- Enzym – 1.11.1.8 in der Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- UniProt P07202
- Sandra M. McLachlan, Yuji Nagayama, Pavel N. Pichurin, Yumiko Mizutori, Chun-Rong Chen, Alexander Misharin, Holly A. Aliesky, Basil Rapoport: The link between Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: a role for regulatory T cells. In: Endocrinology. Band 148, Nr. 12, Dezember 2007, ISSN 0013-7227, S. 5724–5733, doi:10.1210/en.2007-1024, PMID 17823263.
- S. Mariotti, P. Caturegli, P. Piccolo, G. Barbesino, A. Pinchera: Antithyroid peroxidase autoantibodies in thyroid diseases. In: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. Band 71, Nr. 3, September 1990, ISSN 0021-972X, S. 661–669, doi:10.1210/jcem-71-3-661, PMID 2168432.
- KEGG pathway: Autoimmune thyroid disease