Propanole
Propanole sind Alkohole mit drei Kohlenstoffatomen und einer Hydroxygruppe (–OH). Sie haben die allgemeine Summenformel C3H8O und eine molare Masse von 60,10 g/mol. Es gibt nur zwei Isomere:
| Propanole | ||
| Name | 1-Propanol | 2-Propanol |
| Andere Namen | n-Propanol | Isopropanol |
| Strukturformel | 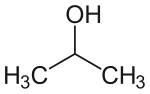 | |
| CAS-Nummer | 71-23-8 | 67-63-0 |
| PubChem | 1031 | 3776 |
| Summenformel | C3H8O | |
| Molare Masse | 60,10 g·mol−1 | |
| Aggregatzustand | flüssig | |
| Schmelzpunkt | −126 °C[1] | −88 °C[2] |
| Siedepunkt | 97 °C[1] | 82 °C[2] |
Einzelnachweise
- Eintrag zu 1-Propanol in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 5. April 2019. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- Eintrag zu 2-Propanol in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 5. April 2019. (JavaScript erforderlich)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.