4-Propylanisol
4-Propylanisol ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Phenolether.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
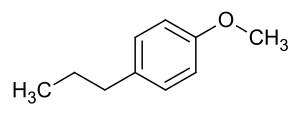 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | 4-Propylanisol | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen | ||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C10H14O | |||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
farblose Flüssigkeit[2] | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 150,22 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig[2] | |||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
0,941 g·cm−3 (25 °C)[2] | |||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
215 °C[2] | |||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit | ||||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,504 (20 °C)[2] | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Toxikologische Daten | ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | ||||||||||||||||
Vorkommen
4-Propylanisol kommt natürlich in manchen Honigsorten und Katsuobushi vor.[4][5][6]
Gewinnung und Darstellung
4-Propylanisol kann durch Hydrierung von Anethol mit einem Nickelkatalysator gewonnen werden.[6]
Verwendung
4-Propylanisol wird als Aromastoff verwendet.[6][7]
Einzelnachweise
- Eintrag zu DIHYDROANETHOLE in der CosIng-Datenbank der EU-Kommission, abgerufen am 24. Oktober 2021.
- Datenblatt p-Propyl anisole, ≥99%, FCC, FG bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 7. Dezember 2019 (PDF).
- David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics A Ready-reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-0595-5, S. 364 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Laïd Boukraâ: Honey in Traditional and Modern Medicine. CRC Press, 2013, ISBN 978-1-4398-4016-0, S. 339 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Yin Yang, Marie-José Battesti u. a.: Characterization of Botanical and Geographical Origin of Corsican “Spring” Honeys by Melissopalynological and Volatile Analysis. In: Foods. 3, 2014, S. 128–148, doi:10.3390/foods3010128.
- George A. Burdock: Encyclopedia of Food and Color Additives. CRC Press, 1997, ISBN 978-0-8493-9414-0, S. 2339 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- S.A. Sangster, J. Caldwell u. a.: The metabolism of p-propylanisole in the rat and mouse and its variation with dose. In: Food and Chemical Toxicology. 21, 1983, S. 263–271, doi:10.1016/0278-6915(83)90059-5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.