3-Hydroxyanthranilat-3,4-Dioxygenase
3-Hydroxyanthranilat-3,4-Dioxygenase (3HAO) (Gen: HAAO) heißt dasjenige Enzym, das 3-Hydroxyanthranilat zu 2-Amino-3-carboxymuconat-semialdehyd oxidiert. Dieser Reaktionsschritt gehört zum Abbau-Stoffwechselweg der Aminosäure Tryptophan, das Reaktionsprodukt ist aber auch Ausgangsstoff für die Biosynthese von Nicotinsäure und NAD. 3HAO kommt in vielen Bakterien, Pilzen und Tieren vor. Beim Menschen wird sie hauptsächlich in der Leber produziert.[1][2]
| 3-Hydroxyanthranilat-3,4-Dioxygenase | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Vorhandene Strukturdaten: 2qnk | ||
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 286 Aminosäuren | |
| Sekundär- bis Quartärstruktur | Monomer | |
| Kofaktor | Fe2+ | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Gen-Name | HAAO | |
| Externe IDs | ||
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 1.13.11.6, Dioxygenase | |
| Reaktionsart | Addition von zwei Sauerstoffatomen | |
| Substrat | 3-Hydroxyanthranilat + O2 | |
| Produkte | 2-Amino-3-carboxymuconat-semialdehyd | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Bakterien, Pilze, Tiere | |
Hemmung der 3HAO mit 4-Chlor-3-hydroxyanthranilat reduzierte die Anhäufung von Chinolinat bei frisch rückenmarkverletzten Mäusen und verbesserte die neurologische Symptomatik.[3]
Katalysierte Reaktion
 + O2
+ O2 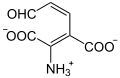
 + H2O
+ H2O
3-Hydroxyanthranilat wird zu einem Semialdehyd oxidiert, der sich spontan zu Chinolinat umlagert.
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- UniProt P46952
- BioGPS Eintrag
- Yates JR, Heyes MP, Blight AR: 4-chloro-3-hydroxyanthranilate reduces local quinolinic acid synthesis, improves functional recovery, and preserves white matter after spinal cord injury. In: J. Neurotrauma. 23, Nr. 6, Juni 2006, S. 866–81. doi:10.1089/neu.2006.23.866. PMID 16774472.