1,1,2,2-Tetrafluorethan
1,1,2,2-Tetrafluorethan ist eine chemische Verbindung des Fluors aus der Gruppe der Fluorkohlenwasserstoffe.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
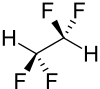 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | 1,1,2,2-Tetrafluorethan | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C2H2F4 | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 102,03 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
gasförmig | |||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
−19,9 °C[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Treibhauspotential |
1337 (bezogen auf 100 Jahre)[3] | |||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||||||||
Gewinnung und Darstellung
1,1,2,2-Tetrafluorethan kann durch Hydrogenolyse von Cryofluoran gewonnen werden.[4]
Verwendung
1,1,2,2-Tetrafluorethan wird wegen seines niedrigeren Dampfdruckes im Gegensatz zu seinem Isomer 1,1,1,2-Tetrafluorethan selten als Kühlmittel verwendet.[5] Es wird zum Schäumen von Polystyrol verwendet.[6]
Einzelnachweise
- David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 85th Edition. CRC Press, 2004, ISBN 978-0-8493-0485-9, S. 6–145 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- SynQuest Labs: 1,1,2,2-Tetrafluoroethane SynQuest Labs, Inc., abgerufen am 25. Juli 2017.
- G. Myhre, D. Shindell et al.: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. Hrsg.: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2013, Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing, S. 24–39; Table 8.SM.16 (ipcc.ch [PDF]).
- D. D. Eley, Herman Pines, Paul B. Weisz: Advances in Catalysis. Academic Press, 1993, ISBN 978-0-08-056543-9, S. 340 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- R.E. Banks, B.E. Smart, J.C. Tatlow: Organofluorine Chemistry Principles and Commercial Applications. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013, ISBN 978-1-4899-1202-2, S. 626 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- United Nations: UNEP 2006 Report of the Rigid and Flexible Foams Technical Options Committee. United Nations Environment Programme Ozone Secretariat, 2007, ISBN 978-92-807-2826-2, S. 24 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.

