Tetracosahexaensäure
Tetracosahexaensäure ist eine langkettige, mehrfach ungesättigte Fettsäure in der Gruppe der Omega-3-Fettsäuren. Die sechs Doppelbindungen sind cis-konfiguriert, sie sind jeweils durch eine Methylengruppe getrennt. Die Polyensäure zählt somit zu den Isolensäuren.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
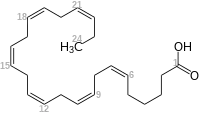 | ||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||
| Name | Tetracosahexaensäure | |||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||
| Summenformel | C24H36O2 | |||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 356,55 g·mol−1 | |||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig[1] | |||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||
Vorkommen
Sie kommt verestert als Triacylglycerid in Fisch und Fischöl und in Stachelhäutern (Echinodermata) vor.[3][4] Sie wurde auch im menschlichem Sperma und im Augapfel nachgewiesen.[3]
Sie wurde von japanischen Forschern 1934 in Fischen entdeckt, welche auch den Namen Nisinsäure (von Nisin[5]) vorschlugen.[6][7]
Gewinnung und Darstellung
Tetracosahexaensäure kann durch eine vierstufige Synthese gewonnen werden.[8]
Einzelnachweise
- Alfa Chemistry: CAS 68378-49-4 6(Z),9(Z),12(Z),15(Z),18(Z),21(Z)-Tetracosahexaenoic acid - Fatty Acid & Lipids / Alfa Chemistry, abgerufen am 29. Januar 2022
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- John W. Blunt, Murray H. G. Munro: Dictionary of Marine Natural Products. Chapman & Hall, 2008, ISBN 978-08493-8216-1, S. 1820.
- Robert G. Ackman: Marine Biogenic Lipids, Fats and Oils. Vol. 1, CRC Press, 1989, ISBN 0-8493-4889-7, S. 118.
- The Etymology of Chemical Names: Tradition and Convenience vs. Rationality in Chemical Nomenclature. Walter de Gruyter & Co KG, 2019, ISBN 978-3-11-061124-3 (books.google.com).
- Georg Borgstrom: Fish As Food V1: Production, Biochemistry,and Microbiology. Elsevier, 2012, ISBN 978-0-323-14280-9, S. 218 (books.google.com).
- Yoshiyuki Toyama, Tomotaro Tsuchiya: The highly unsaturated acids in sardine oil. xl the constitution of nisinic acid c24h36o2 in sardine oil. In: Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. Band 10, Nr. 11, 1935, ISSN 0009-2673, S. 547–551, doi:10.1246/bcsj.10.547 (csj.jp).
- Toshimasa Itoh, Ayako Tomiyasu, Keiko Yamamoto: Efficient Synthesis of the Very-Long-Chain n-3 Fatty Acids, Tetracosahexaenoic Acid (C24:6n-3) and Tricosahexaenoic Acid (C23:6n-3). In: Lipids. Band 46, Nr. 5, 2011, ISSN 0024-4201, S. 455–461, doi:10.1007/s11745-011-3541-5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.