Fosmidomycin
Fosmidomycin ist ein Antibiotikum aus Streptomyces lavendulae, einer Streptomyceten-Art.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
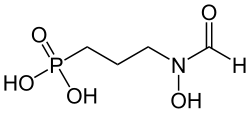 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Freiname | Fosmidomycin | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
[3-(N-Hydroxyformamido)propyl]-phosphonsäure | |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C4H10NO5P | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Arzneistoffangaben | ||||||||||||||||
| Wirkstoffklasse | ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 183,10 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||||||||
Es hemmt den Methylerythritolphosphatweg, der zur Biosynthese der Terpengrundbausteine Isopentenylpyrophosphat (IPP) und Dimethylallylpyrophosphat (DMAPP) führt. Dieser findet sich z. B. im Plasmodium falciparum, dem Erreger der Malaria.
Die Grundbausteine IPP und DMAPP sind an der Bildung von Hormonen, Cholesterin, Zellmembranen und Proteinstrukturen beteiligt. Fehlen diese, muss der Malariaerreger sterben.[2][3][4] Das Enzym, welches von Fosmidomycin inhibiert wird, ist die Desoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphat-Reduktase.
Einzelnachweise
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- S Borrmann, et al.: Fosmidomycin-clindamycin for Plasmodium falciparum infections in African children. In: J Infect Dis. 189, Nr. 5, 2004, S. 901–908. doi:10.1086/381785.
- S Borrmann, et al.: Fosmidomycin plus clindamycin for treatment of pediatric patients aged 1 to 14 years with Plasmodium falciparum malaria. In: Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 50, Nr. 8, 2006, S. 2713–2718. doi:10.1128/AAC.00392-06.
- R Ruangweerayut, et al.: Assessment of the pharmacokinetics and dynamics of two combination regimens of fosmidomycin-clindamycin in patients with acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria. In: Malaria J. 7, 2008, S. 225. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-7-225.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.