Batanta
Batanta ist mit 453 km² die kleinste der vier Hauptinseln des Archipels Raja Ampat vor der Küste Westneuguineas (Indonesien).[1]
| Batanta | ||
|---|---|---|
 Topographisches Kartenblatt (1942) | ||
| Gewässer | Halmaherasee, Pazifischer Ozean | |
| Inselgruppe | Raja Ampat | |
| Geographische Lage | 0° 52′ S, 130° 40′ O | |
| ||
| Fläche | 453 km² | |
| Höchste Erhebung | Gunung Batanta 1184 m | |
| Hauptort | Jodlo | |
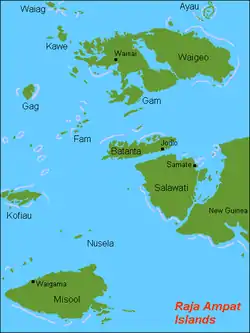 Raja-Ampat-Inseln mit Batanta in der Kartenmitte | ||
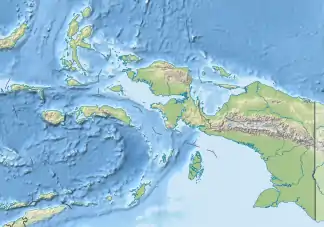
Batanta liegt zwischen den Inseln Salawati im Süden und Gam und Waigeo im Norden. Weiter südöstlich befindet sich die Vogelkopfhalbinsel Neuguineas. Der Archipel gehört zum Regierungsbezirk Raja Ampat der Provinz Westpapua.
Die höchste Erhebung Batanas erreicht 1184 m.
Fauna
Auf der Insel ist der Blaue Baumwaran (Varanus macraei) beheimatet. Diese Spezies ist bisher nur von Batanta bekannt.
Weitere endemische Arten der Insel sind die in Süßwasser lebenden Regenbogenfische Melanotaenia batanta und Melanotaenia synergos, während Melanotaenia catherinae auch von der Nachbarinsel Waigeo bekannt ist. Auch der Nacktkopf-Paradiesvogel und der Roter Paradiesvogel kommen sowohl auf Batanta als auch auf Waigeo vor.[2][3]
Einzelnachweise
- sunda-islands.com Lexikon
- Clifford B. Frith, Bruce M. Beehler: The Birds of Paradise - Paradisaeidae. Oxford University Press, Oxford 1998, ISBN 0-19-854853-2, S. 402.
- Clifford B. Frith, Bruce M. Beehler: The Birds of Paradise - Paradisaeidae. Oxford University Press, Oxford 1998, ISBN 0-19-854853-2, S. 476.