Alpha-Latrotoxin
Alpha-Latrotoxin (α-LTX) ist ein Nervengift und Hauptbestandteil des von Spinnen der Gattung Echte Witwen (Latrodectus) in den Giftdrüsen produzierten Giftgemischs.
| Alpha-Latrotoxin | ||
|---|---|---|
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 1381 Aminosäuren | |
| Sekundär- bis Quartärstruktur | Homotetramer | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Externe IDs | ||
| Transporter-Klassifikation | ||
| TCDB | 1.C.63 | |
| Bezeichnung | Latrotoxine | |
Wirkungsweise
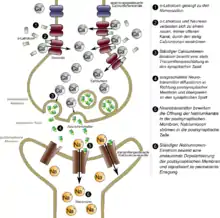
Alpha-Latrotoxin ist ein relativ großmolekulares Protein, das seine Wirkung am peripheren Nervensystem entfaltet. Es wirkt als Toxin, indem es in der präsynaptischen Nervenzelle zusätzliche Calcium-Kanäle öffnet, an deren Struktur das Toxin wahrscheinlich selbst maßgeblich beteiligt ist und die besonders für Calciumionen (Ca2+) durchlässig sind. Durch den Calciumionen-Einstrom in die Zelle werden ständig Neurotransmitter abgegeben (Exozytose), was ein andauerndes nervöses Signal in Form von hohen Aktionspotentialfrequenzen zur Folge hat. Es kommt zu Krämpfen. Zum Tod führt das Gift, wenn die Krämpfe das Atemsystem befallen und zur Erstickung (durch Atemstillstand oder durch Ödeme) führen.
Literatur
- E. V. Grishin: Black widow spider toxins: the present and the future. In: Toxicon. 36 (11), November 1998, S. 1693–1701. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(98)00162-7. PMID 9792186.
- T. C. Südhof: alpha-Latrotoxin and its receptors: neurexins and CIRL/latrophilins. In: Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 2001, S. 933–962. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.933. PMID 11520923.
- Y. A. Ushkaryov, K. E. Volynski, A. C. Ashton: The multiple actions of black widow spider toxins and their selective use in neurosecretion studies. In: Toxicon. 43 (5), April 2004, S. 527–542. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.02.008. PMID 15066411.
- Y. A. Ushkaryov, A. Rohou, S. Sugita: α-Latrotoxin and its receptors". Handbook of experimental pharmacology. In: Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 184 (184), 2008, S. 171–206. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-74805-2_7, ISBN 978-3-540-74804-5. PMC 2519134 (freier Volltext). PMID 18064415.
- A. W. Henkel, Sethuraman Sankaranarayanan: Mechanisms of alpha-latrotoxin action. In: Cell and tissue research. 296 (2), May 1999, S. 229–233. doi:10.1007/s004410051284. PMID 10382267.
- M. E. Peterson: Black widow spider envenomation. In: Clinical techniques in small animal practice. 21 (4), November 2006, S. 187–190. doi:10.1053/j.ctsap.2006.10.003. PMID 17265903.
- H. Hiramatsu, S. Tadokoro, M. Nakanishi, N. Hirashima: Latrotoxin-induced exocytosis in mast cells transfected with latrophilin. In: Toxicon. 56 (8), December 2010, S. 1372–1380. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2010.08.002. PMID 20708026.
- G. A. Jelinek: Widow spider envenomation (latrodectism): a worldwide problem. In: Wilderness & environmental medicine. 8 (4), November 1997, S. 226–231. doi:10.1580/1080-6032(1997)008[0226:WSELAW]2.3.CO;2. PMID 11990169.
- A. Rohou, J. Nield, Y. A. Ushkaryov: Insecticidal toxins from black widow spider venom. In: Toxicon. 49 (4), March 2007, S. 531–549. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.11.021. PMC 2517654 (freier Volltext). PMID 17210168.
- S. Gasparini, N. Kiyatkin, P. Drevet u. a.: The low molecular weight protein which co-purifies with alpha-latrotoxin is structurally related to crustacean hyperglycemic hormones. In: J. Biol. Chem. 269 (31), August 1994, S. 19803–19809. PMID 8051061.
- Andis Graudins, Michelle J. Little, Sandy S. Pineda, Peter G. Hains, Glenn F. King, Kevin W. Broady, Graham M. Nicholson: Cloning and Activity of a Novel α-latrotoxin from Red-back Spider Venom. In: Biochemical Pharmacology. 83 (1), 1 January 2012, S. 170–183. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.09.024. PMID 22001442.
- Rüdiger Wehner, Walter Gering: Zoologie. 24. Auflage. Georg Thieme Verlag KG, Stuttgart 2007, ISBN 978-3-13-367424-9, S. 404.