6-Aminopenicillansäure
Bei der 6-Aminopenicillansäure (6-APA) handelt es sich um den Grundbaustein der Penicilline.[3] Mithilfe von 6-APA und eines Präkursors (Kopplungsstück) können alle semisynthetischen Penicilline wie z. B. Ampicillin oder Amoxicillin hergestellt werden. 6-APA wurde 1958 von G. N. Rolinson beschrieben und als Patent angemeldet.[4][5]
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
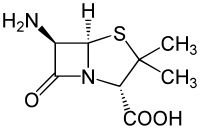 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | 6-Aminopenicillansäure | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
(2S,5R,6R)-6-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptan-2-carbonsäure | ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C8H12N2O3S | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
beiger Feststoff[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 216,26 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
schwer löslich in Wasser (2,46 g·l−1 bei 20 °C)[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Toxikologische Daten | |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||||||||
Synthese
6-APA wird sowohl enzymatisch als auch chemisch durch Hydrolyse von Penicillin G hergestellt.[6] Bei der enzymatischen Hydrolyse reagiert Penicillin G mit Wasser zu 6-APA und Phenylessigsäure. Die chemische Hydrolyse erfolgt bei niedrigen Temperaturen mit Trimethylchlorsilan, Phosphorpentachlorid und Dichlormethan.[7] Die enzymatische Hydrolyse erfolgt mit der Penicillin-G-Acylase.[8] Aufgrund der hochreaktiven, schwer zulagernden und toxischen Stoffe sowie benötigten Temperaturen von −50 °C wird die biotechnologische Herstellung mit der Penicillin-G-Acylase bevorzugt. Die Ausbeute beider Methoden liegt zwischen 80 und 90 %.[9]
Einzelnachweise
- Datenblatt (+) - 6- Aminopenicillanic acid, 96% bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 1. März 2016 (PDF).
- Europäisches Arzneibuch, Deutscher Apotheker Verlag Stuttgart, 6. Ausgabe, 2008, S. 527, ISBN 978-3-7692-3962-1.
- F. R. Batchelor, F. P. Doyle, J. H. C. Nayler, G. N. Rolinson: Synthesis of Penicillin: 6-Aminopenicillanic Acid in Penicillin Fermentations. In: Nature. Band 183, Nr. 4656, 24. Januar 1959, S. 257–258, doi:10.1038/183257b0.
- G. N. Rolinson, A. M. Geddes: The 50th anniversary of the discovery of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA). In: International journal of antimicrobial agents. Band 29, Nummer 1, Januar 2007, S. 3–8, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2006.09.003. PMID 17137753.
- Patent US2941995: Recovery of solid 6-aminopenicillanic acid. Angemeldet am 22. Juli 1958, veröffentlicht am 21. Juni 1960, Anmelder: Beecham Research Laboratories, Erfinder: Frank Peter Doyle, John Herbert Charles Nayler, George Newbolt Rolinson.
- A. Nandi, S. Pan, R. Potumarthi, M. K. Danquah, I. P. Sarethy: A Proposal for Six Sigma Integration for Large-Scale Production of Penicillin G and Subsequent Conversion to 6-APA. In: Journal of analytical methods in chemistry. 2014, S. 413616, doi:10.1155/2014/413616. PMID 25057428, PMC 4099176 (freier Volltext).
- A. Brugging, E. C. Roos, E. de Vroom: Penicillin acylase in the industrial production of β-lactam antibiotics. In: Organic Process Research and Development. 2(2), 1998, S. 128–133.
- K. Srirangan, V. Orr, L. Akawi, A. Westbrook, M. Moo-Young, C. P. Chou: Biotechnological advances on penicillin G acylase: pharmaceutical implications, unique expression mechanism and production strategies. In: Biotechnology Advances. Band 31, Nummer 8, Dezember 2013, S. 1319–1332, doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.05.006. PMID 23721991.
- R. P. Elander: Industrial production of beta-lactam antibiotics. In: Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. Band 61, Nummer 5–6, Juni 2003, S. 385–392, doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1274-y. PMID 12679848.