Squalen-Monooxygenase
Die Squalen-Monooxygenase (Squalenepoxidase, SE) ist das Enzym, das die Oxidation von Squalen zu S-Squalen-2,3-epoxid katalysiert. Diese Reaktion findet in Eukaryoten und manchen Bakterien statt; in Tieren ist sie Teil der Cholesterinbiosynthese. Im Mensch ist SE in den Mikrosomen lokalisiert.[1][2][3]
| Squalen-Monooxygenase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 574 Aminosäuren | |
| Kofaktor | FAD | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Gen-Name | SQLE | |
| Externe IDs | ||
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 1.14.99.7, Monooxygenase | |
| Reaktionsart | Addition eines Sauerstoffatoms | |
| Substrat | Squalen + red.Acc./H2 + O2 | |
| Produkte | Squalenepoxid + ox.Acc. + H2O | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Eukaryoten, wenige Bakterien[1] | |
Katalysierte Reaktion
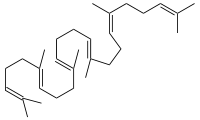 + AH2 + O2 ⇔
+ AH2 + O2 ⇔ -Squalen-2%252C3-epoxid.svg.png.webp) + A + H2O
+ A + H2O
Squalen wird zu (S)-Squalen-2,3-epoxid oxidiert, der Acceptor wird dehydriert.
Weblinks
Wikibooks: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie: Cholesterinbiosynthese – Lern- und Lehrmaterialien
- Jassal / reactome: Squalene is oxidized to its epoxide
Einzelnachweise
- InterPro-Eintrag
- Lamb DC, Jackson CJ, Warrilow AG, Manning NJ, Kelly DE, Kelly SL: Lanosterol biosynthesis in the prokaryote Methylococcus capsulatus: insight into the evolution of sterol biosynthesis. In: Mol. Biol. Evol.. 24, Nr. 8, August 2007, S. 1714–21. doi:10.1093/molbev/msm090. PMID 17567593.
- UniProt Q14534
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.