SEA native peptide ligation
Die SEA native peptide ligation ist eine biochemische Methode zur Proteinligation durch Verknüpfung von zwei oder mehreren Peptiden.
Eigenschaften
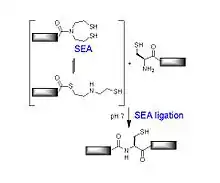
Das N-terminale Peptid muss für die Proteinligation als letzte Aminosäure (an seinem C-Terminus) eine bis(2-Sulfanylethyl)aminogruppe (SEA) und das C-terminale Peptid muss für die Proteinligation als erste Aminosäure (an seinem N-Terminus) ein Cystein oder Homocystein aufweisen. Im Zuge der Ligation bildet sich am SEA-Peptid eine Thioester-Bindung, die sich umestert und anschließend zur Peptidbindung umlagert (Thiotransesterifikation und S,N-acyl shift). Als Katalysator wird Mercaptophenylessigsäure (MPAA) verwendet.
Alternative Verfahren zur Proteinligation wurden beschrieben, z. B. die native chemical ligation, der Prior Thiol Capture, die Expressed Protein Ligation,[1] das Acyl-Initiated Capture und die Peptidligation mit Selenocystein.[2]
Geschichte
Die wurde unabhängig voneinander ab 2010 von der Arbeitsgruppe um O. Melnyk und der Arbeitsgruppe um C. F. Liu entwickelt.[3][4]
Einzelnachweise
- T. W. Muir, D. Sondhi, P. A. Cole: Expressed protein ligation: a general method for protein engineering. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Band 95, Nummer 12, Juni 1998, ISSN 0027-8424, S. 6705–6710, PMID 9618476, PMC 22605 (freier Volltext).
- B. L. Nilsson, M. B. Soellner, R. T. Raines: Chemical synthesis of proteins. In: Annual review of biophysics and biomolecular structure. Band 34, 2005, ISSN 1056-8700, S. 91–118, doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.34.040204.144700, PMID 15869385, PMC 2845543 (freier Volltext).
- N. Ollivier, J. Dheur, R. Mhidia, A. Blanpain, O. Melnyk: Bis(2-sulfanylethyl)amino native peptide ligation. In: Organic letters. Band 12, Nummer 22, November 2010, ISSN 1523-7052, S. 5238–5241, doi:10.1021/ol102273u, PMID 20964289.
- W. Hou, X. Zhang, F. Li, C. F. Liu: Peptidyl N,N-bis(2-mercaptoethyl)-amides as thioester precursors for native chemical ligation. In: Organic letters. Band 13, Nummer 3, Februar 2011, ISSN 1523-7052, S. 386–389, doi:10.1021/ol102735k, PMID 21175148.