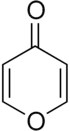
Pyrone
Pyrone oder Pyranone sind eine Gruppe cyclischer chemischer Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der sauerstoffhaltigen Heterocyclen.
Pyrone enthalten einen ungesättigten Sechsring mit einem Sauerstoffatom und einer Ketogruppe. Es existieren zwei isomere Verbindungen: 2-Pyron und 4-Pyron. Die 2-Pyron-Struktur kommt in der Natur als Teil des Cumarin-Ringsystems und als Teil mehrerer bakterieller Signalmoleküle vor. 4-Pyron kommt ebenfalls in einigen natürlichen chemischen Verbindungen wie Maltol, Kojisäure und Flavonoiden vor.
Die 4-Pyron-Struktur ist ein Bestandteil der Mekonsäure. Die Biosynthese erfolgt aus Phenylalanin oder Tyrosin.[1]
Literatur
- Introduction to Organic Chemistry, Andrew Streitwieser, Jr. and Clayton H. Heathcock, Third Edition, S. 1038–1040. ISBN 0-02-418140-4.
- Alexander O Brachmann, Sophie Brameyer u. a.: Pyrones as bacterial signaling molecules. In: Nature Chemical Biology. 2013, S. 573–578, doi:10.1038/nchembio.1295.
Einzelnachweise
- J. K. Weng, Y. Li, H. Mo, C. Chapple: Assembly of an evolutionarily new pathway for α-pyrone biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. In: Science. Band 337, Nummer 6097, August 2012, S. 960–964, doi:10.1126/science.1221614, PMID 22923580.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.