Polyphenoloxidase
Phenolase, genauer chloroplastische Polyphenoloxidase (PPO), früher: Catecholoxidase, heißt das Homolog der Tyrosinase in Pflanzen. Zusätzlich zu den Reaktionen der Tyrosinase ist sie in der Lage, Phenole und Catechole zu oxidieren. Diese Reaktionen sind verantwortlich für die Bräunung von Pflanzenmaterial nach Verletzung und Kontakt mit Luftsauerstoff. Die entstehenden Chinone sind giftig für pathogene Mikroorganismen.[1]
| Phenolase der Süßkartoffel (Ipomoea batatas) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 496 Aminosäuren | |
| Sekundär- bis Quartärstruktur | Monomer | |
| Kofaktor | 2 Kupfer | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Externe IDs | ||
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 1.10.3.1, Oxidoreduktase | |
| Reaktionsart | Oxidation | |
| Substrat | 2 Mono/Diphenol + O2 | |
| Produkte | 2 o-Dichinon + 2 H2O | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Pflanzen | |
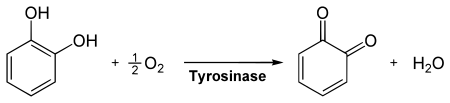
Enzymatische Katalyse
Bei der Oxidation von Brenzcatechin in Anwesenheit von Phenolase als Katalysator wird das Dihydroxybenzol in Benzochinon umgewandelt:
Einzelnachweise
- Mayer AM: Polyphenol oxidases in plants and fungi: going places? A review. In: Phytochemistry. 67, Nr. 21, November 2006, S. 2318–2331. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.08.006. PMID 16973188.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.