Photoaffinitätsmarkierung
Eine Photoaffinitätsmarkierung ist eine biochemische Methode zur Molekülmarkierung durch einen UV-Licht-aktivierten Label-Transfer oder eine Vernetzung eines Moleküls nach Bindung eines anderen Moleküls in vivo oder in vitro.
Prinzip
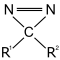
Proteine und andere Moleküle binden mit einer jeweils bestimmten Affinität an andere Moleküle. Die Photoaffinitätsmarkierung verwendet photoreaktive Moleküle (z. B. Arylazide, Diazirine) als eine der reaktiven Gruppen eines Vernetzers bei Proteinen, um den Zeitpunkt der Vernetzung besser steuern zu können, da die Vernetzung erst mit einer UV-Bestrahlung ausgelöst wird.[1] Aus Arylaziden entstehen bei UV-Bestrahlung reaktive Nitrene, aus Diazirinen reaktive Carbene. Aufgrund der geringeren Selektivität der radikalischen Vernetzer wird oftmals die Funktionsfähigkeit des Proteins durch Reaktion des radikalischen Vernetzers mit wichtigen Funktionen (z. B. ein aktives Zentrum oder eine Bindungsstelle) gemindert. Daher werden photoreaktive Vernetzer meistens eingesetzt, wenn keine oder nur eine Amin- oder Sulfhydrylgruppe zur selektiven Vernetzung zur Verfügung steht oder eine anschließende Funktionsfähigkeit unerheblich ist. Der Vernetzer kann dabei anschließend selektiv spaltbar sein oder zur erleichterten Identifikation noch weitere signaltragende Teile (Reportermoleküle) enthalten, z. B. radioaktive Isotope oder Fluorophore.[2] Durch Zugabe von Radikalfängern kann die affine Bindung des Vernetzers überprüft werden.[3]
Es existieren auch photoreaktive Diazirin-enthaltende Analoga der Aminosäuren Leucin (Photo-Leucin), Methionin und p-Benzoyl-Phenylalanin, die bereits während der Translation in vivo in das Protein eingebaut werden können.[4] Die Aminosäurederivate werden per metabolischer Markierung durch Fütterung mit den photoreaktiven Aminosäurederivaten und erniedrigten Konzentrationen der jeweiligen unmodifizierten Aminosäure erzeugt. Die Proteincharakterisierung erfolgt meistens durch Massenspektrometrie,[5] Western Blot[6] oder Proteinsequenzierung.[7]
Bei der Entwicklung einer Photoaffinitätsmarkierung ist die chemische Stabilität der Reportermoleküle bei der Kopplung an die photoreaktive Gruppe ein Entwicklungsziel.[8]
Geschichte
Die Photoaffinitätsmarkierung wurde 1962 von Frank Westheimer entwickelt.[9][10] Ab 1969 wurden Arylazide zur Markierung von Antikörpern verwendet.[11][12]
Literatur
- Vila-Perello, M., et al. (2007). Covalent capture of phospho-dependent protein oligomerization by site-specific incorporation of a diazirine photo-cross-linker. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(26):8068–69.
- Bomgarden, R. (2008). Studying Protein Interactions in Living Cells. In: Gen. Eng. News., Band 28, Nummer 7.
- P.-O. Hétu, et al. (2008) Photo-crosslinking of proteins in intact cells reveals a dimeric structure of cyclooxygenase-2 and an inhibitor-sensitive oligomeric structure of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1. In: Arch Biochem Biophys. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2008.04.038
- Weaver, M.S., et al. (2008) The copper-binding domain of sparc mediates cell survival in vitro via interaction with integrin beta 1 and activation of integrin-linked kinase. In: J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M706563200
Einzelnachweise
- J. Sumranjit, S. J. Chung: Recent advances in target characterization and identification by photoaffinity probes. In: Molecules. Band 18, Nummer 9, 2013, S. 10425–10451. doi:10.3390/molecules180910425. PMID 23994969.
- J. B. Denny, Günter Blobel: 125I-labeled crosslinking reagent that is hydrophilic, photoactivatable, and cleavable through an azo linkage. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Band 81, Nummer 17, September 1984, S. 5286–5290. PMID 6433347. PMC 391688 (freier Volltext).
- A. E. Ruoho, H. Kiefer, P. E. Roeder, S. J. Singer: The mechanism of photoaffinity labeling. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Band 70, Nummer 9, September 1973, S. 2567–2571, ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 4517671. PMC 427057 (freier Volltext).
- M. Suchanek, A. Radzikowska, C. Thiele: Photo-leucine and photo-methionine allow identification of protein–protein interactions in living cells. In: Nature Methods. 2, Nr. 4, 2005, S. 261–268. doi:10.1038/nmeth752. PMID 15782218.
- D. Robinette, N. Neamati, K. B. Tomer, C. H. Borchers: Photoaffinity labeling combined with mass spectrometric approaches as a tool for structural proteomics. In: Expert review of proteomics. Band 3, Nummer 4, August 2006, S. 399–408. doi:10.1586/14789450.3.4.399. PMID 16901199. PMC 2266983 (freier Volltext).
- S. J. Evans, F. L. Moore: Nonradioactive photoaffinity labeling of steroid receptors using western blot detection system. In: Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.). Band 176, 2001, S. 261–272. doi:10.1385/1-59259-115-9:261. PMID 11554327.
- M. Dong, L. J. Miller: Direct demonstration of unique mode of natural peptide binding to the type 2 cholecystokinin receptor using photoaffinity labeling. In: Peptides. Band 46, August 2013, S. 143–149. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2013.06.007. PMID 23770253. PMC 3739435 (freier Volltext).
- Haijun Guo, Zhengqiu Li: Developments of bioorthogonal handle-containing photo-crosslinkers for photoaffinity labeling. In: Med. Chem. Commun. 2017, doi:10.1039/C7MD00217C.
- A. Singh, E. R. Thornton, F. H. Westheimer: The photolysis of diazoacetylchymotrypsin. In: The Journal of biological chemistry. Band 237, September 1962, S. 3006–3008. PMID 13913310. PDF.
- R. J. Vaughan, F. H. Westheimer: A method for marking the hydrophobic binding sites of enzymes. An insertion into the methyl group of an alanine residue of trypsin. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. Band 91, Nummer 1, Januar 1969, S. 217–218. PMID 5782459.
- G. W. J. Fleet, R. R. Porter, J. R. Knowles: Affinity Labelling of Antibodies with Aryl Nitrene as Reactive Group. In: Nature. 224, 1969, S. 511–512, doi:10.1038/224511a0.
- C. A. Converse, F. F. Richards: Two-stage photosensitive label for antibody combining sites. In: Biochemistry. Band 8, Nummer 11, November 1969, S. 4431–4436. PMID 4187591.