N-Methylserotonin
5-Hydroxy-N-Methyltryptamin (kurz N-Methylserotonin), auch Norbufotenin ist ein Alkaloid aus der Tryptamin-Familie. Es ist ein Derivat des Serotonins. Geläufig ist auch die Bezeichnung Nω-Methylserotonin, um es von Tryptamin abgeleiteten Verbindungen zu unterscheiden, in denen eine Methylgruppe an das Stickstoffatom der Indol-Gruppe gebunden ist.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
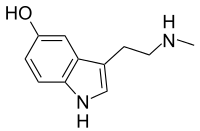 | ||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||
| Name | N-Methylserotonin | |||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||
| Summenformel | C11H14N2O | |||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Arzneistoffangaben | ||||||||||
| Wirkstoffklasse | ||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 190.24 g·mol−1 | |||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||
Vorkommen


N-Methylserotonin kommt in Pflanzen, Tieren und Pilzen vor, unter anderem Actaea racemosa (Trauben-Silberkerze)[2], Zanthoxylum piperitum (Szechuanpfeffer)[3], Litoria aurea (Gold-Laubfrosch)[4] und Amanita-Pilzen (Wulstlinge).[5]
Pharmakologie
Aus pharmakologischer Sicht bindet sich N-Methylserotonin an mehrere Serotonin-Rezeptoren, darunter die 5-HT1A- und die 5-HT7-Rezeptoren mit hoher Affinität (IC50 ≤ 2 nM) und Selektivität. Neben der serotonergen Aktivität wirkt die Verbindung außerdem als Serotonin-Wiederaufnahmehemmer.
Einzelnachweise
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- S. L. Powell, T. Gödecke, D. Nikolic, S. N. Chen, S. Ahn, B. Dietz, N. R. Farnsworth, R. B. van Breemen, D. C. Lankin, G. F. Pauli, J. L. Bolton: In vitro serotonergic activity of black cohosh and identification of N(omega)-methylserotonin as a potential active constituent. In: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. Band 56, Nummer 24, Dezember 2008, ISSN 1520-5118, S. 11718–11726, doi:10.1021/jf803298z. PMID 19049296, PMC 3684073 (freier Volltext) .
- E Yanase, M Ohno, H Harakawa, SI Nakatsuka: Isolation of N,N-dimethyl and N-methylserotonin 5-O-β-glucosides from immature Zanthoxylum piperitum seeds. In: Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 74, Nr. 9, 2010, S. 1951–2. doi:10.1271/bbb.100261. PMID 20834148.
- McClean, Stephen; Robinson, Robert C.; Shaw, Chris; Smyth, W. Franklin: Characterization and determination of indole alkaloids in frog-skin secretions by electrospray ionization ion trap mass spectrometry. In: Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry. 16, Nr. 5, 2002, S. 346–354. doi:10.1002/rcm.583. PMID 11857717.
- Tyler, V. E., Jr.; Groeger, D.: Amanita alkaloids. II. Amanita citrina and Amanita porphyria. In: Planta Medica. 12, Nr. 4, 1964, S. 397–402. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1100193.