Metaraminol
Metaraminol (Handelsnamen Aramine und Araminon) ist ein Arzneistoff aus der Gruppe der Sympathomimetika zur Behandlung von zu niedrigem Blutdruck (Hypotonie).
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
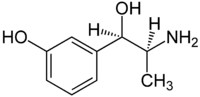 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Freiname | Metaraminol | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel |
| |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Arzneistoffangaben | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC-Code |
C01CA09 | |||||||||||||||
| Wirkstoffklasse | ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | ||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Toxikologische Daten | ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||||||||
Metaraminol ist nicht für die Behandlung einer Dauererektion (Priapismus), zugelassen, es existieren jedoch Fallberichte von erfolgreicher Anwendung.[3][4][5] Der Wirkstoff wird zudem zur Provokation eines vermuteten Familiären Mittelmeerfiebers (FMF) angewendet.[6][7] Dabei wird dem Patienten eine einmalige 10-mg-Dosis verabreicht; erfolgt während der nächsten 48 Stunden ein Anfall, ist dies ein Hinweis für das Vorliegen von FMF.
Einzelnachweise
- The Merck Index. An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 14. Auflage, 2006, S. 1024, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1.
- Datenblatt Metaraminol (+)-bitartrate salt bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 10. April 2011 (PDF).
- McDonald M, Santucci R: Successful management of stuttering priapism using home self-injections of the alpha-agonist metaraminol.. In: Int Braz J Urol. 30, Nr. 2, 2004, S. 121–2. doi:10.1590/S1677-55382004000200007. PMID 15703094.
- Koga S, Shiraishi K, Saito Y: Post-traumatic priapism treated with metaraminol bitartrate: case report.. In: The Journal of Trauma. 30, Nr. 12, 1990, S. 1591–3. doi:10.1097/00005373-199012000-00029. PMID 2258979.
- Block T, Sturm W, Ernst G, Staehler G, Schmiedt E: [Metaraminol in therapy of various forms of priapism]. In: Urologe A. 27, Nr. 4, 1988, S. 225–9. PMID 3140463.
- Barakat MH, El-Khawad AO, Gumaa KA, El-Sobki NI, Fenech FF: Metaraminol provocative test: a specific diagnostic test for familial Mediterranean fever. In: Lancet. 1, Nr. 8378, 1984, S. 656–7. PMID 6142351.
- Huppertz HI, Michels H: [The metaraminol provocation test in the diagnosis of familial Mediterranean fever]. In: Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 136, Nr. 5, 1988, S. 243–5. PMID 3405225.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.