Glucane
Glucane sind Oligo- oder Polysaccharide, die nur aus D-Glucose-Molekülen aufgebaut und durch glycosidische Bindungen miteinander verknüpft sind.[1] Analog dazu besteht die Stoffgruppe der Fructane aus Fructose-Monomeren und die Galactane aus Galactose-Monomeren.
Typen
Eine Klassifizierung kann nach Art der glycosidischen Bindung erfolgen:
Alpha-Glucane
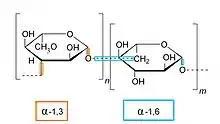
Dextran mit alpha-glycosidischen Bindungen
Folgende Glucane besitzen eine α-glycosidische Bindung:
Beta-Glucane
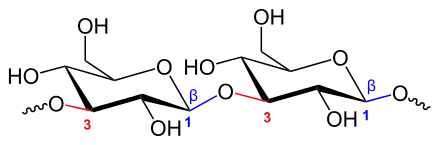
Beispiel eines β-Glucans, des Curdlans; hervorgehoben sind die Beta-Glucanbindungen
Folgende Beta-Glucane besitzen eine β-glycosidische Bindung und sind teils in der Medizin von Bedeutung:
- Cellulose, β-1,4-Glucan
- Chitin, β-1,4-Glucan
- Curdlan, β-1,3-Glucan
- Laminarin, β-1,3- und β-1,6-Glucan
- Chrysolaminarin, β-1,3-Glucan
- Lentinan, ein aufgereinigtes β-1,6:β-1,3-Glucan, isoliert aus Lentinula edodes
- Lichenin, β-1,3- und β-1,4-Glucan
- Pleuran, β-1,3- und β-1,6-Glucan, isoliert aus Pleurotus ostreatus
- Zymosan, β-1,3-Glucan
- Schizophyllan, β-1,3- und β-1,6-Glucan[2]
- Scleroglucan, β-1,3- und β-1,6-Glucan[3]
Einzelnachweise
- MeSH Glucane
- Munenori Numata, Teruaki Hasegawa, Tomohisa Fujisawa, Kazuo Sakurai, Seiji Shinkai: β-1,3-Glucan (Schizophyllan) Can Act as a One-Dimensional Host for Creation of Novel Poly(aniline) Nanofiber Structures. In: Organic Letters, 6 (24), 2004, S. 4447–4450, doi:10.1021/ol0483448.
- Tommasina Coviello, Antonio Palleschi, Mario Grassi, Pietro Matricardi, Gianfranco Bocchinfuso, Franco Alhaique: Scleroglucan: A Versatile Polysaccharide for Modified Drug Delivery. In: Molecules, 10 (1), 2005, S. 6–33, doi:10.3390/10010006.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.