Diphosphomevalonat-Decarboxylase
Die Diphosphomevalonat-Decarboxylase (MDDase) ist das Enzym, das in den meisten Lebewesen die Umwandlung von Diphosphomevalonat zum Isopentenyldiphosphat katalysiert. In Eukaryoten ist diese Reaktion Teil der Biosynthese der Isoprenoide, speziell in Tieren Teil der Cholesterinbiosynthese. Im Mensch wird MDDase in Herz, Lunge, Leber, Muskeln, Hirn, Pankreas, Nieren und Plazenta exprimiert und ist, im Gegensatz zu aufwärts im Syntheseweg gelegenen Enzymen, nicht in den Peroxisomen, sondern im Zytosol lokalisiert.[2][3]
| Diphosphomevalonat-Decarboxylase | ||
|---|---|---|
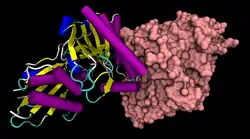 | ||
| Bänder-/Oberflächenmodell des Dimer nach PDB 3D4J | ||
|
Vorhandene Strukturdaten: 3D4J | ||
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 399 Aminosäuren | |
| Sekundär- bis Quartärstruktur | Homodimer | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Gen-Name | MVD | |
| Externe IDs | ||
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 4.1.1.33, Lyase | |
| Reaktionsart | Decarboxylierung | |
| Substrat | ATP + Diphosphomevalonat | |
| Produkte | ADP + Isopentenyldiphosphat + Pi + CO2 | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Lebewesen[1] | |
| Orthologe | ||
| Mensch | Hausmaus | |
| Entrez | 4597 | 192156 |
| Ensembl | ENSG00000167508 | ENSMUSG00000006517 |
| UniProt | P53602 | Q99JF5 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_002461 | NM_13865 |
| Refseq (Protein) | NP_002452 | NP_619597 |
| Genlocus | Chr 16: 88.65 – 88.66 Mb | Chr 8: 122.43 – 122.44 Mb |
| PubMed-Suche | 4597 | 192156 |
Katalysierte Reaktion
![]() + ATP ⇒
+ ATP ⇒ ![]() + ADP + Pi + CO2
+ ADP + Pi + CO2
5-Diphospho-R-mevalonat wird zu Isopentenyldiphosphat (IPP) umgesetzt.
Weblinks
Wikibooks: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie: Cholesterinbiosynthese – Lern- und Lehrmaterialien
- Jassal / reactome: Mevalonate-5-pyrophosphate is decarboxylated
Einzelnachweise
- Homologe bei OMA
- UniProt P53602
- Hogenboom S, Tuyp JJ, Espeel M, Koster J, Wanders RJ, Waterham HR: Human mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase is localized in the cytosol. In: Mol. Genet. Metab.. 81, Nr. 3, März 2004, S. 216–24. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2003.12.001. PMID 14972328.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.