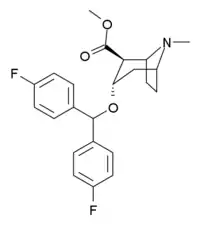
Difluoropin
Difluoropin (auch: O-620) ist ein Stimulans, das chemisch-strukturell von den Tropan-Alkaloiden abgeleitet ist. Es wird aus Tropinon synthetisiert, das als selektiver Dopamin-Wiederaufnahmehemmer wirkt. Auch Difluoropin ist ein Dopamin-Wiederaufnahmehemmer, wobei nicht das (R)-Enantiomer für die Wirkung verantwortlich ist, wie das bei Kokain der Fall ist, sondern das (S)-Enantiomer.[2] Es ist mit Benzatropin strukturell verwandt und wirkt wie diese auch anticholinerg und antihistaminisch.[3]
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||
| Freiname | Difluoropin | ||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
(1S,2S,3S,5R)-3-[Bis(4-fluorphenyl)methoxy]-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-2-carbonsäuremethylester | ||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C23H25F2NO3 | ||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Arzneistoffangaben | |||||||||||||
| Wirkstoffklasse | |||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 401,45 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||
Es konnte nachgewiesen werden, dass Difluoropin bei Tieren stimulierend wirkt, jedoch weniger stark als andere Phenyltropane, etwa WIN 35,428 oder RTI-55.[4] Difluoropin konnte bei Tieren die Symptome der Parkinson-Krankheit lindern.[5]
Einzelnachweise
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- P. C. Meltzer, A. Y. Liang, B. K. Madras: The discovery of an unusually selective and novel cocaine analog: difluoropine. Synthesis and inhibition of binding at cocaine recognition sites. In: Journal of medicinal chemistry. Band 37, Nummer 13, Juni 1994, S. 2001–2010, PMID 8027983.
- V. C. Campbell, T. A. Kopajtic, A. H. Newman, J. L. Katz: Assessment of the influence of histaminergic actions on cocaine-like effects of 3α-diphenylmethoxytropane analogs. In: The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. Band 315, Nummer 2, November 2005, S. 631–640, doi:10.1124/jpet.105.090829, PMID 16055673.
- Katz, J.L.; Izenwasser, S.; Kline, R.H.; Allen, A.C.; Newman, A.H.: Novel 3α-diphenylmethoxytropane analogs: selective dopamine uptake inhibitors with behavioral effects distinct from those of cocaine. In: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (Jan. 1999; 288(1)), S. 302–315, PMID 9862785.
- Madras, B.K.; Fahey, M.A.; Goulet, M.; Lin, Z.; Bendor, J.; Goodrich, C.; Meltzer, P.C.; Elmaleh, D.R.; Livni, E; Bonab, A.A.; Fischman, A.J.: Dopamine transporter (DAT) inhibitors alleviate specific parkinsonian deficits in monkeys: association with DAT occupancy in vivo. In: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. (November 2006; 319(2)), S. 570–585, PMID 16885433.