CD88
CD88 (synonym C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1, C5aR1) ist ein Oberflächenprotein und beteiligt am Komplementsystem der Immunantwort.
| C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Andere Namen |
C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor, C5a-R, C5aR | |
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 350 Aminosäuren, 39.336 Da | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Externe IDs | ||
| Orthologe (Mensch) | ||
| Entrez | 728 | |
| Ensembl | ENSG00000197405 | |
| UniProt | P21730 | |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_001736.3 | |
| Refseq (Protein) | NP_001727.1 | |
| PubMed-Suche | 728 | |
Eigenschaften
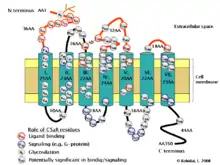
CD88 ist der Rezeptor für das Anaphylatoxin C5a und weist zwei Kontaktstellen für C5a auf. Am N-Terminus von CD88 ist eine Bindungsstelle mit vergleichsweise hoher Affinität und in der Nähe der Transmembrandomäne von CD88 ist eine Bindungsstelle niedrigerer Affinität, die für die Signaltransduktion des CD88 innerhalb der Zelle verantwortlich ist. Eine Bindung von C5a an CD88 führt zu einer verstärkten Chemotaxis, einer verstärkten Degranulation, einem Anstieg der zytosolischen Konzentration an Calciumionen und einer verstärkten Bildung von Superoxid. Es ist beteiligt an der Entzündung, Ontogenese und der Entstehung von Übergewicht und Krebs.[1][2][3] CD88 ist ein G-Protein-gekoppelter Rezeptor[4] mit sieben Transmembrandomänen (ein heptahelikaler Rezeptor).[5] CD88 ist glykosyliert, phosphoryliert und sulfatiert. CD88 wird von verschiedenen Zelltypen gebildet, darunter Granulozyten, Monozyten, dendritischen Zellen, Astrozyten, und von der Zelllinie HepG2[6] sowie Makrophagen und T-Zellen.[7]
Verschiedene Agonisten und Antagonisten für CD88 wurden beschrieben.[8][9][10]
Einzelnachweise
- Brennan FH, Gordon R, Lao HW, Biggins PJ, Taylor SM, Franklin RJ, Woodruff TM, Ruitenberg MJ: The Complement Receptor C5aR Controls Acute Inflammation and Astrogliosis following Spinal Cord Injury. In: The Journal of Neuroscience. 35, Nr. 16, April 2015, S. 6517–31. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5218-14.2015. PMID 25904802.
- Lim J, Iyer A, Suen JY, Seow V, Reid RC, Brown L, Fairlie DP: C5aR and C3aR antagonists each inhibit diet-induced obesity, metabolic dysfunction, and adipocyte and macrophage signaling. In: FASEB Journal. 27, Nr. 2, February 2013, S. 822–31. doi:10.1096/fj.12-220582. PMID 23118029.
- Markiewski MM, DeAngelis RA, Benencia F, Ricklin-Lichtsteiner SK, Koutoulaki A, Gerard C, Coukos G, Lambris JD: Modulation of the antitumor immune response by complement. In: Nature Immunology. 9, Nr. 11, November 2008, S. 1225–35. doi:10.1038/ni.1655. PMID 18820683. PMC 2678913 (freier Volltext).
- T. M. Woodruff, K. S. Nandakumar, F. Tedesco: Inhibiting the C5-C5a receptor axis. In: Molecular immunology. Band 48, Nummer 14, August 2011, S. 1631–1642, doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2011.04.014, PMID 21549429.
- C. Gerard, N. P. Gerard: C5A anaphylatoxin and its seven transmembrane-segment receptor. In: Annual review of immunology. Band 12, 1994, S. 775–808, doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.004015, PMID 8011297.
- Klos A, Wende E, Wareham KJ, Monk PN: International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. [corrected]. LXXXVII. Complement peptide C5a, C4a, and C3a receptors. In: Pharmacological Reviews. 65, Nr. 1, January 2013, S. 500–43. doi:10.1124/pr.111.005223. PMID 23383423.
- P. N. Monk, A. M. Scola, P. Madala, D. P. Fairlie: Function, structure and therapeutic potential of complement C5a receptors. In: British journal of pharmacology. Band 152, Nummer 4, Oktober 2007, S. 429–448, doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707332, PMID 17603557, PMC 2050825 (freier Volltext).
- Wong AK, Finch AM, Pierens GK, Craik DJ, Taylor SM, Fairlie DP: Small molecular probes for G-protein-coupled C5a receptors: conformationally constrained antagonists derived from the C terminus of the human plasma protein C5a. In: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 41, Nr. 18, August 1998, S. 3417–25. doi:10.1021/jm980065. PMID 9719594.
- Gong Y, Barbay JK, Buntinx M, Li J, Wauwe JV, Claes C, Lommen GV, Hornby PJ, He W: Design and optimization of aniline-substituted tetrahydroquinoline C5a receptor antagonists. In: Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 18, Nr. 14, July 2008, S. 3852–5. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.06.059. PMID 18595693.
- Sumichika H, Sakata K, Sato N, Takeshita S, Ishibuchi S, Nakamura M, Kamahori T, Ehara S, Itoh K, Ohtsuka T, Ohbora T, Mishina T, Komatsu H, Naka Y: Identification of a potent and orally active non-peptide C5a receptor antagonist. In: The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277, Nr. 51, December 2002, S. 49403–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209672200. PMID 12384495.