Aminocyclopropancarbonsäure
Die 1-Aminocyclopropan-1-carbonsäure (ACC) ist ein Zwischenprodukt bei der Biosynthese des Pflanzenhormons Ethylen. Ausgangspunkt für ihre Synthese ist die Aminosäure Methionin. Die Biosynthese wird im Detail unter Ethylen beschrieben. ACC wirkt auch als partieller Agonist am tierischen NMDA-Rezeptor.[2]
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
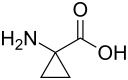 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Aminocyclopropancarbonsäure | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
ACC | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C4H7NO2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 101,1 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Einzelnachweise
- Datenblatt Aminocyclopropancarbonsäure bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 8. März 2011 (PDF).
- A. Inanobe, H. Furukawa, E. Gouaux: Mechanism of Partial Agonist Action at the NR1 Subunit of NMDA Receptors. In: Neuron 47, S. 71–84 (2005)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.
