5-Carboxamidotryptamin
5-Carboxamidotryptamin (5-CT) ist ein Tryptaminderivat, das eng mit dem Neurotransmitter Serotonin verwandt ist.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
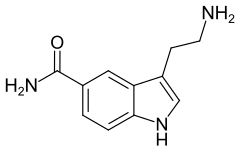 | |||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||
| Name | 5-Carboxamidotryptamin | ||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C11H13N3O | ||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 203,245 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||
5-CT wirkt als nicht-selektiver, hochaffiner Vollagonist an den 5-HT1A-, 5-HT1B-, 5-HT1D-, 5-HT5A- und 5-HT7-Rezeptoren sowie mit geringerer Affinität an den 5-HT2-, 5-HT3- und 5-HT6-Rezeptoren.[2][3][4] Er hat eine vernachlässigbare Affinität zu den 5-HT1E- und 5-HT1F-Rezeptoren.[5] 5-CT bindet am stärksten an den 5-HT1A-Rezeptor und es wurde einst angenommen, dass es für diese Stelle selektiv ist.[6][7]
Einzelnachweise
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- J. Yamada, Y. Sugimoto, T. Noma, T. Yoshikawa: Effects of the non-selective 5-HT receptor agonist, 5-carboxamidotryptamine, on plasma glucose levels in rats. In: European Journal of Pharmacology. Band 359, Nr. 1, 16. Oktober 1998, S. 81–86, doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00617-7, PMID 9831297.
- Christine E. Wright, James A. Angus: 5-Carboxamidotryptamine Elicits 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 Receptor-Mediated Cardiovascular Responses in the Conscious Rabbit: Evidence for 5-HT Release from Platelets. In: Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. Band 13, Nr. 4, April 1989, S. 557–564 (lww.com [abgerufen am 10. Mai 2021]).
- Serotonin Receptor Subtypes and Ligands. Abgerufen am 10. Mai 2021 (englisch).
- J. A. Stanton, D. N. Middlemiss, M. S. Beer: Autoradiographic localization of 5-CT-insensitive 5-HT1-like recognition sites in guinea pig and rat brain. In: Neuropharmacology. Band 35, Nr. 2, Februar 1996, S. 223–229, doi:10.1016/0028-3908(95)00178-6, PMID 8734492.
- David R Thomas, Derek N Middlemiss, Stephen G Taylor, Paul Nelson, Anthony M Brown: 5-CT stimulation of adenylyl cyclase activity in guinea-pig hippocampus: evidence for involvement of 5-HT7 and 5-HT1A receptors. In: British Journal of Pharmacology. Band 128, Nr. 1, September 1999, S. 158–164, doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0702759, PMID 10498847, PMC 1571602 (freier Volltext).
- P. R. Saxena, A. Lawang: A comparison of cardiovascular and smooth muscle effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-carboxamidotryptamine, a selective agonist of 5-HT1 receptors. In: Archives internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Thérapie. Band 277, Nr. 2, Oktober 1985, S. 235–252, PMID 2933009.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.