1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat
1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat ist eine ionische Flüssigkeit (auch: ionic liquid oder Flüssigsalz), also ein Salz, dessen Schmelzpunkt unter 100 °C liegt.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
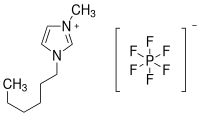 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C10H19F6N2P | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
gelbe Flüssigkeit[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 312,24 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
1,419 g·cm−3[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||||||||
Eigenschaften
Auf Grund des geringen Schmelzpunkts handelt es sich bei 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat um eine Raumtemperatur-ionische Flüssigkeit (RTIL). Als polare, hydrophobe Flüssigkeit wird es, wie viele ionische Flüssigkeiten, als Lösungsmittel in der Synthese eingesetzt.
Darstellung
1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat kann durch eine Anionenmetathese ausgehend von 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazoliumbromid und einem Hexafluorophosphat-Salz gewonnen werden.[3]
Verwendung
Es kann in Extraktionsprozessen in Kombination mit 4,4,4-Trifluor-1-(2-thienyl)-1,3-butanedion verwendet werden, um divalente Metallkationen zu extrahieren.[4] Außerdem wird die Anwendung von 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat in Trennungsprozessen von Alkanen und aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffen diskutiert.[5]
Einzelnachweise
- Datenblatt 1-Hexyl-3-methyl-imidazolium-hexafluorophosphat bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 26. November 2021 (PDF).
- Gonçalo V. S. M. Carrera, Raquel F. M. Frade, João Aires-de-Sousa, Carlos A. M. Afonso, Luis C. Branco: Synthesis and properties of new functionalized guanidinium based ionic liquids as non-toxic versatile organic materials. In: Tetrahedron. Band 66, Nr. 45, 2010, ISSN 0040-4020, S. 8785–8794, doi:10.1016/j.tet.2010.08.040.
- Hideaki Shirota, Shohei Kakinuma, Kotaro Takahashi, Akito Tago, Hocheon Jeong, Tomotsumi Fujisawa: Ultrafast Dynamics in Aromatic Cation Based Ionic Liquids: A Femtosecond Raman-Induced Kerr Effect Spectroscopic Study. In: Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. Band 89, Nr. 9, 2016, ISSN 0009-2673, S. 1106–1128, doi:10.1246/bcsj.20160085.
- Naoki Hirayama, Mika Deguchi, Hitomi Kawasumi, Takaharu Honjo: Use of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate room temperature ionic liquids as chelate extraction solvent with 4,4,4-trifluoro-1-(2-thienyl)-1,3-butanedione. In: Talanta. Band 65, Nr. 1, 2005, ISSN 0039-9140, S. 255–260, doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2004.06.015.
- Yi Li, Li-Sheng Wang, Yun-Xia Feng, Chun-Yuan Zhang: Activity Coefficients of Organic Solutes at Infinite Dilution in Ionic Liquids. 1. 1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Hexafluorophosphate and 1-Octyl-3-Methylimidazolium Hexafluorophosphate and Their Application to Alkane/Aromatic and Aromatic/Aromatic Hydrocarbon Separation. In: Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. Band 50, Nr. 18, 2011, ISSN 0888-5885, S. 10755–10764, doi:10.1021/ie102458k.
