Vanillin-Dehydrogenase
Eine Vanillin-Dehydrogenase (VDH, EC 1.2.1.67) ist ein Enzym, das die Umsetzung von Vanillin zur Vanillinsäure katalysiert. Die Dehydrogenase gehört zur Familie der Oxidoreduktasen.
| Vanillin-Dehydrogenase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 482 Aminosäuren (in Pseudomonas putida Stamm KT2440) | |
| Kofaktor | NAD+ | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Externe IDs |
| |
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 1.2.1.67, Oxidoreduktase | |
| Substrat | Vanillin, H2O | |
| Produkte | Vanillinsäure, 2 H+ | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Pseudomonas | |
Für die Reaktion wird als Cofaktor NAD+ benötigt, das zu NADH reduziert wird:
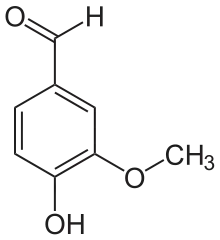 + NAD+ + H2O
+ NAD+ + H2O 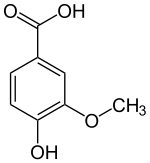 + NADH + H+
+ NADH + H+
Das Enzym wurde unter anderem in Pseudomonas putida sowie Pseudomonas fluorescens nachgewiesen. Dort ist Vanillin ein Zwischenprodukt beim Abbau von Ferulasäure zu Protocatechusäure, welche dann nach Ringspaltung weiter metabolisiert wird.[1][2]
Das Fehlen des Cofaktors NAD+ reduziert die enzymatische Aktivität in P. fluorescens.[1]
Homologe Enzyme wurden auch bei Burkholderia-Arten gefunden und gehören allgemein zu den Aldehyddehydrogenasen.[3]
Einzelnachweise
- A. Narbad, M. J. Gasson: Metabolism of ferulic acid via vanillin using a novel CoA-dependent pathway in a newly-isolated strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens. In: Microbiology. 144 (Pt 5), 1998, S. 1397–1405. PMID 9611814; (PDF, freier Volltextzugriff, engl.)
- R. Plaggenborg, J. Overhage, A. Steinbüchel, H. Priefert: Functional analyses of genes involved in the metabolism of ferulic acid in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. In: Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 61 (5–6), 2003, S. 528–535. PMID 12764569; doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1260-4.
- Homologe bei OMA
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.