Sapogenine
Sapogenine sind chemische Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Triterpene. Sapogenine sind die Aglykone der Saponine, z. B. aus dem chilenischen Seifenbaum Quillaja saponaria. Beispiele für Sapogenine sind Quillajasäure,[1] Gypsogenin, Yamogenin[2] Tiggenin, Neogitogenin, Tokorogenin, Diosgenin, Hecogenin oder Digitogenin.
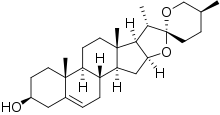
das Sapogenin Yamogenin
Einzelnachweise
- W. Karrer: Konstitution und Vorkommen der organischen Pflanzenstoffe (exclusive Alkaloide). Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-034-85142-8, S. 817.
- Roland Hardman, Ezekiel Abayomi Sofowora: Isolation and characterization of yamogenin from balanites aegyptiaca. In: Phytochemistry. 9, Nr. 3, März 1970, S. 645–649. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)85706-4.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.