Ribosephosphat-Diphosphokinase
Die Ribosephosphat-Diphosphokinase (PRS-1) (früher -Pyrophosphokinase) ist das Enzym, das in allen Lebewesen die Synthese von PRPP aus Ribose-5-phosphat katalysiert. Diese Reaktion ist Grundlage für die Biosynthese aller Nukleotide. Im Mensch sind noch zwei Isoformen von PRS-1 bekannt. Mutationen im PRPS1-Gen können zu einer Überaktivität des Enzyms, und diese zu erhöhtem erblichem Risiko für Gicht führen. Andere PRPS1-Mutationen verringern die Enzymaktivität und sind die Ursache für das so genannte Rosenberg-Chutorian-Syndrom und eine Form der Gehörlosigkeit (ARTS-Syndrom).[2]
| Ribosephosphat-Diphosphokinase | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Vorhandene Strukturdaten: s. UniProt | ||
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 317 Aminosäuren | |
| Sekundär- bis Quartärstruktur | Homodimer | |
| Kofaktor | Mg2+ | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Gen-Name | PRPS1 | |
| Externe IDs | ||
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 2.7.6.1, Diphosphotransferase | |
| Reaktionsart | Übertragung von Diphosphat | |
| Substrat | Ribose-5-phosphat + ATP | |
| Produkte | PRPP + AMP | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Lebewesen[1] | |
Katalysierte Reaktion
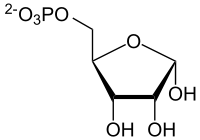 + ATP ⇔
+ ATP ⇔ 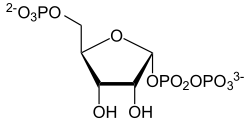 + AMP
+ AMP
α-D-Ribose-5-phosphat wird zu α-D-5-Phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphat umgesetzt.
Weblinks
Wikibooks: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie: alpha-D-5-Phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphat – Lern- und Lehrmaterialien
- d'Eustachio / reactome: 5-Phosphoribose 1-diphosphate biosynthesis
- OrphaNet: Arts-Syndrom
- OrphaNet: PRPP synthase superactivity
Einzelnachweise
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.