Penicillin-bindendes Protein
Ein Penicillin-bindendes Protein (PBP) ist ein Protein, das Penicillin binden kann.[2]
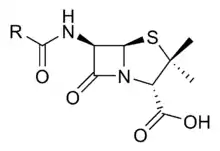
Eigenschaften
Penicillin-bindende Proteine binden mit mittlerer bis hoher Affinität an β-Lactam-Antibiotika, mit Ausnahme von Tabtoxinin-β-Lactam. Penicillin-bindende Proteine besitzen eine PASTA-Proteindomäne (englisch PBP and Serine/Threonine kinase Associated domain ‚‘) zur Bindung der β-Lactam-Antibiotika.[3] Die PASTA-Domäne ist typisch für Penicillin-bindende Proteine und Proteinkinase-B-artige Proteine, woher das Akronym des Namens der Domäne stammt.[3] Penicillin-bindende Proteine sind meist Proteine der letzten Schritte der Biosynthese des Peptidoglykans in der bakteriellen Zellwand,[4][5] z. B. die Murein-Transpeptidase.
Beispiele
In Escherichia coli kommen mindestens sechs PBP zwischen 40 kDa und 91 kDa vor.[6] Darunter sind eine D-Alanin-Carboxypeptidase, eine Peptidoglykan-Transpeptidase und eine Peptidoglykan-Endopeptidase. In Mycobacterium smegmatis wurde ein PBP von 49,5 kDa beschrieben.[7] Das PBP Penicillin binding protein 2A (PBP2A) ist an der Antibiotikum-Resistenz von MRSA beteiligt.[8]
In Mitochondrien von Säugetieren existiert das Protein LACTB, ein Homolog des PBP-βL.[9]
Einzelnachweise
- Sainsbury, S., Bird, L., Rao, V., Shepherd, S.M., Stuart, D.I., Hunter, W.N., Owens, R.J., and Ren, J.: Crystal Structures of Penicillin-Binding Protein 3 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Comparison of Native and Antibiotic-Bound Forms. In: J. Mol. Biol.. 405, 2011, S. 173–184. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.10.024.
- J. M. Frère, M. G. Page: Penicillin-binding proteins: evergreen drug targets. In: Current Opinion in Pharmacology. Band 18C, Oktober 2014, S. 112–119, doi:10.1016/j.coph.2014.09.012, PMID 25450065.
- C. Yeats, R. D. Finn, A. Bateman: The PASTA domain: a beta-lactam-binding domain. In: Trends in Biochemical Sciences. Band 27, Nummer 9, September 2002, S. 438, PMID 12217513.
- E. Sauvage, F. Kerff, M. Terrak, J. A. Ayala, P. Charlier: The penicillin-binding proteins: structure and role in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. In: FEMS microbiology reviews. Band 32, Nummer 2, März 2008, S. 234–258, doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00105.x, PMID 18266856.
- A. Zapun, C. Contreras-Martel, T. Vernet: Penicillin-binding proteins and beta-lactam resistance. In: FEMS microbiology reviews. Band 32, Nummer 2, März 2008, S. 361–385, doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00095.x, PMID 18248419.
- B. G. Spratt: Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. In: European Journal of Biochemistry. Band 72, Nummer 2, Januar 1977, S. 341–352, PMID 319999.
- J. Basu, R. Chattopadhyay, M. Kundu, P. Chakrabarti: Purification and partial characterization of a penicillin-binding protein from Mycobacterium smegmatis. In: Journal of bacteriology. Band 174, Nummer 14, Juli 1992, S. 4829–4832, PMID 1624470, PMC 206282 (freier Volltext).
- H. F. Chambers: Penicillin-binding protein-mediated resistance in pneumococci and staphylococci. In: The Journal of Infectious Diseases. Band 179 Suppl 2, März 1999, S. S353–S359, doi:10.1086/513854, PMID 10081507.
- N. Peitsaro, Z. Polianskyte, J. Tuimala, I. Pörn-Ares, J. Liobikas, O. Speer, D. Lindholm, J. Thompson, O. Eriksson: Evolution of a family of metazoan active-site-serine enzymes from penicillin-binding proteins: a novel facet of the bacterial legacy. In: BMC Evolutionary Biology. Band 8, 2008, S. 26, doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-26, PMID 18226203, PMC 2266909 (freier Volltext).